[置顶] 泰晓 RISC-V 实验箱,配套 30+ 讲嵌入式 Linux 系统开发公开课
Section GC 分析 - Part 3 引用建立过程
Corrector: TinyCorrect v0.2-rc2 - [spaces] Author: 谭源 tanyuan98@outlook.com Date: 2022/06/15 Revisor: Falcon falcon@tinylab.org Project: RISC-V Linux 内核剖析 Sponsor: PLCT Lab, ISCAS
概述
本文为 解决 Linux 内核 Section GC 失败问题 系列文章的一部分。
- Section GC 分析 - Part 1 原理简介
- Section GC 分析 - Part 2 gold 源码解析
- Section GC 分析 - Part 3 引用建立过程
- 解决 Linux 内核 Section GC 失败问题 - Part 1
- 解决 Linux 内核 Section GC 失败问题 - Part 2
上一篇文章 我们介绍了在开启 --gc-sections 选项后,gold 链接器删除未使用到的 section 的过程。
这篇文章我们将结合 ld.bfd 链接器(即默认使用的 ld)源码,探索链接器建立引用关系的过程。
准备工作
下载代码
wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/binutils/binutils-2.40.tar.gz
tar xvf binutils-2.40.tar.gz
cd binutils-2.40/
或者克隆 binutils 仓库
git clone https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/git/binutils-gdb.git
编译
make all-ld -j
编译生成的 ld.bfd 链接器位于 ld/ld-new。
配置调试环境
编写一个用来测试的程序 test.c:
int fun1()
{
return 0;
}
int fun2()
{
return 0;
}
int un_used(){
return 0;
}
int main(){
fun1();
fun2();
return 0;
}
fun1() 和 fun2() 都被 main() 调用了,需要在 GC 过程中保留;un_used() 函数没有被使用过,需要在 GC 过程中删除。
和上一篇文章一样,我们编写一个配置文件,让我们能直接在 VSCode 中进行调试。具体使用方法可以参考 上一篇文章。
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "GDB BFD",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/ld/ld-new",
"args": [
"--gc-sections",
"-dynamic-linker",
"/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2",
"-pie",
"/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1/../../../../lib/Scrt1.o",
"/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1/../../../../lib/crti.o",
"/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1/crtbeginS.o",
"-L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1",
"-L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1/../../../../lib",
"-L/lib/../lib",
"-L/usr/lib/../lib",
"-L/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1/../../..",
"test.o",
"-lgcc_s",
"-lc",
"-lgcc",
"/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1/crtendS.o",
"/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/13.1.1/../../../../lib/crtn.o"
],
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing"
}
],
"stopAtEntry": false
}
]
}
术语解释
符号(Symbol):符号通常指代一个变量或者函数的名称。例如,在 C 语言中,当声明一个函数或变量,编译器会把它们的名称保存为符号。符号表是一个保存了所有符号及其相关信息的数据结构,链接器主要通过它来寻找和解决引用。
重定位(Relocation):在编译和链接过程中,重定位是一个重要步骤。当编译器编译源代码时,它并不知道每个符号最后会被放置在内存的什么位置。因此,编译器生成的对象文件中,会包含一些需要在链接过程中被填充真正地址的占位符,这些占位符就需要重定位。例如,如果一个函数调用了另一个函数,编译器在编译时可能并不知道被调用的函数在内存中的真正地址,所以它会生成一个占位符。然后在链接过程中,链接器会找到被调用函数的真正地址,替换掉占位符,完成重定位。
重定位条目(Relocation Entry):汇编器遇到最终位置未知的目标引用,会生成一个重定位条目,告诉链接器在将目标文件合并成可执行文件时如何修改这个引用。
typedef struct { Elf64_Addr r_offset; // 需要被修改的引用的节偏移 Elf64_Xword r_info; // 存储符号表索引和重定位类型。 Elf64_Sxword r_addend; } Elf64_Rela;
函数调用链分析
elflink.c 中的 _bfd_elf_gc_mark() 函数显而易见是用来标记已经用到的 section 的。
bool
_bfd_elf_gc_mark (struct bfd_link_info *info,
asection *sec,
elf_gc_mark_hook_fn gc_mark_hook)
{
bool ret;
asection *group_sec, *eh_frame;
sec->gc_mark = 1;
/* Mark all the sections in the group. */
group_sec = elf_section_data (sec)->next_in_group;
if (group_sec && !group_sec->gc_mark)
if (!_bfd_elf_gc_mark (info, group_sec, gc_mark_hook))
return false;
/* Look through the section relocs. */
ret = true;
eh_frame = elf_eh_frame_section (sec->owner);
if ((sec->flags & SEC_RELOC) != 0
&& sec->reloc_count > 0
&& sec != eh_frame)
{
struct elf_reloc_cookie cookie;
if (!init_reloc_cookie_for_section (&cookie, info, sec))
ret = false;
else
{
for (; cookie.rel < cookie.relend; cookie.rel++)
if (!_bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc (info, sec, gc_mark_hook, &cookie))
{
ret = false;
break;
}
fini_reloc_cookie_for_section (&cookie, sec);
}
}
if (ret && eh_frame && elf_fde_list (sec))
{
struct elf_reloc_cookie cookie;
if (!init_reloc_cookie_for_section (&cookie, info, eh_frame))
ret = false;
else
{
if (!_bfd_elf_gc_mark_fdes (info, sec, eh_frame,
gc_mark_hook, &cookie))
ret = false;
fini_reloc_cookie_for_section (&cookie, eh_frame);
}
}
eh_frame = elf_section_eh_frame_entry (sec);
if (ret && eh_frame && !eh_frame->gc_mark)
if (!_bfd_elf_gc_mark (info, eh_frame, gc_mark_hook))
ret = false;
return ret;
}
我们暂时不关心它的逻辑,先看看它的调用链。
在该函数处打断点,一直 continue 到 sec.name 为 .text.main。
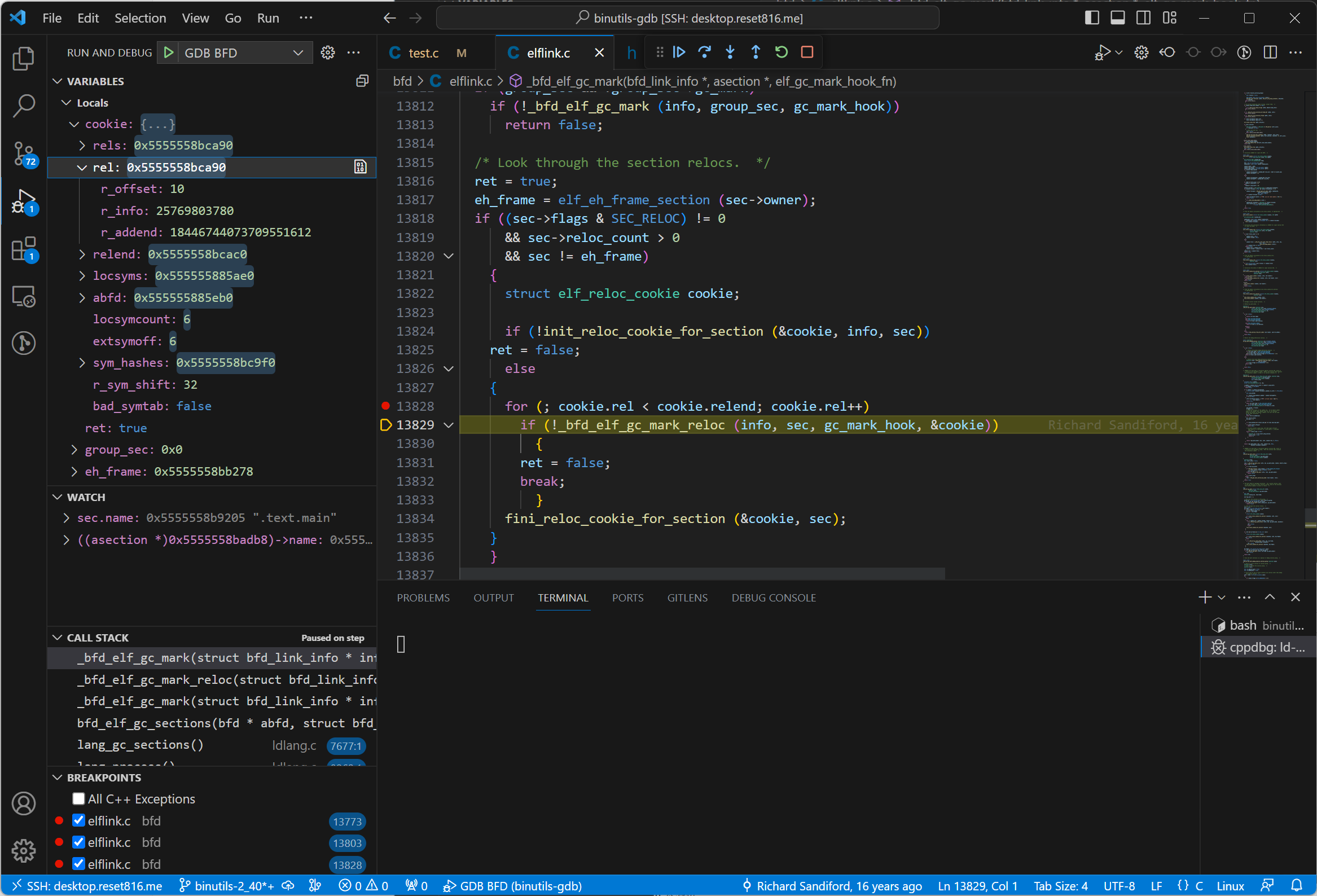
可以看到左下方的调用栈,有两个 _bfd_elf_gc_mark() 在栈中,r_offset 为 10。
如果在 13829 行继续运行,进入函数 _bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc() 后,该函数又会调用一次 _bfd_elf_gc_mark()。
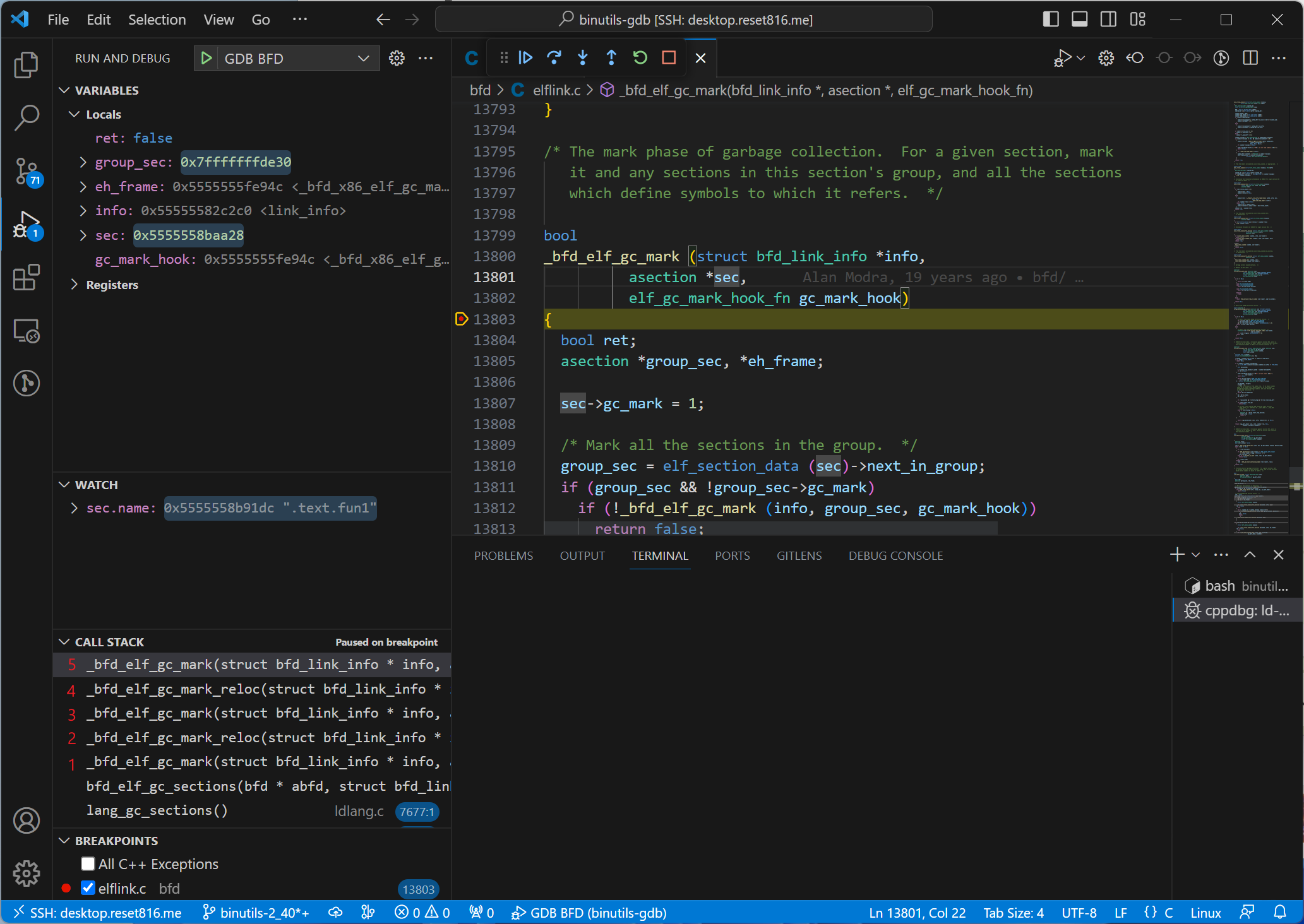
这又向调用栈压入了两个 frame,有了三个 _bfd_elf_gc_mark() 栈。点击左侧的 Call Stack 某一项可以切换栈,查看不同栈的值。
frame | sec.name |
|---|---|
frame 5 | .text.fun1 |
frame 3 | .text.main |
frame 1 | .text |
上表是不同 frame 下变量 sec.name 的值,表示当前 frame 处理的 section 名。说明此时压入了栈正在处理 .text.fun1。
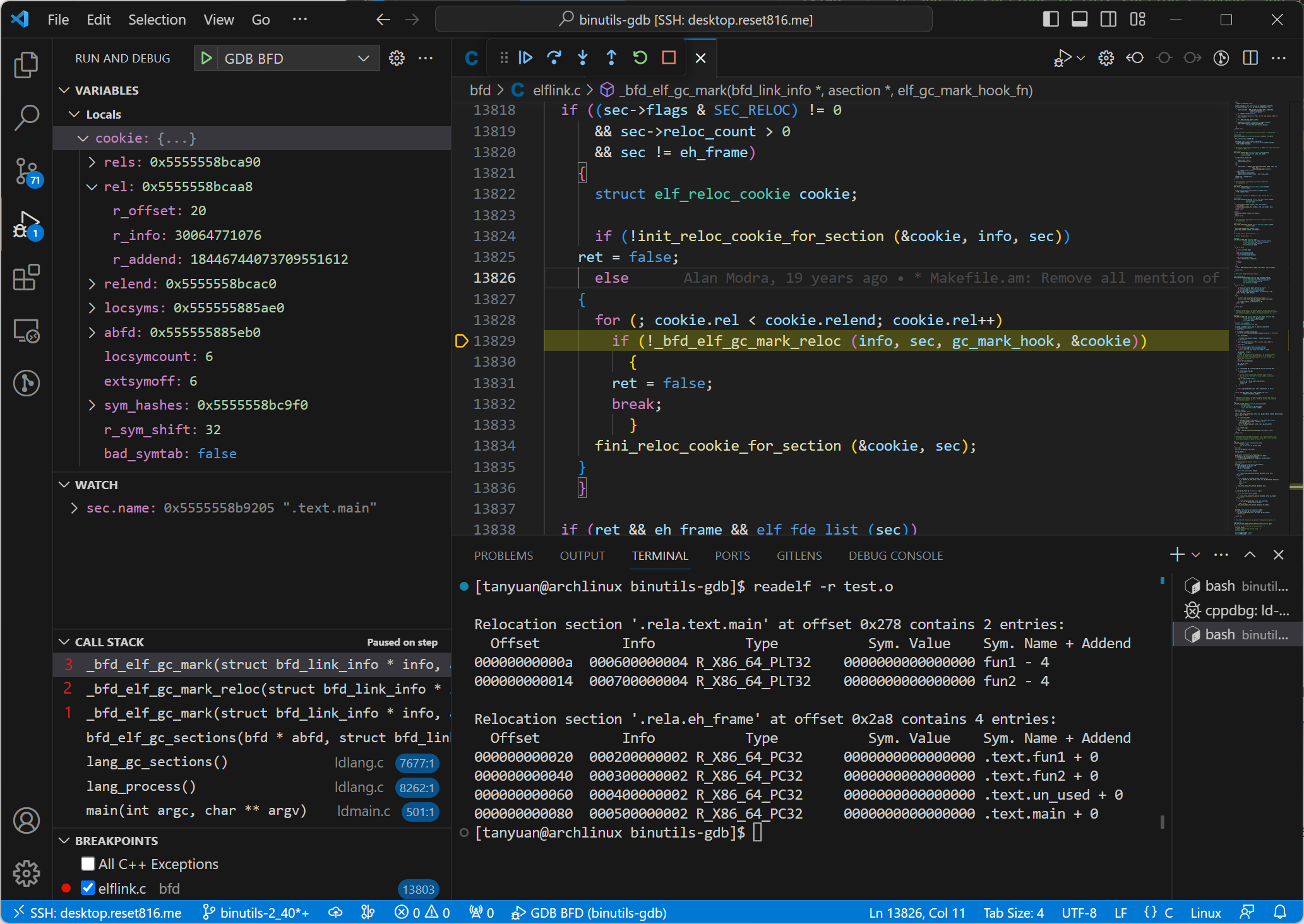
等到 frame 5 和 frame 4 执行完,返回到 frame 3 执行时,for 循环 cookie.rel 执行了++操作,这里又开始遍历 .text.main 的下一个引用。从上图我们可以得知,该引用项的 r_offset 为 20。这里调用 _bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc() 函数,该函数又会调用 _bfd_elf_gc_mark() 来处理这个引用,即压入新的栈,重新建立了 frame 4 和 frame 5。
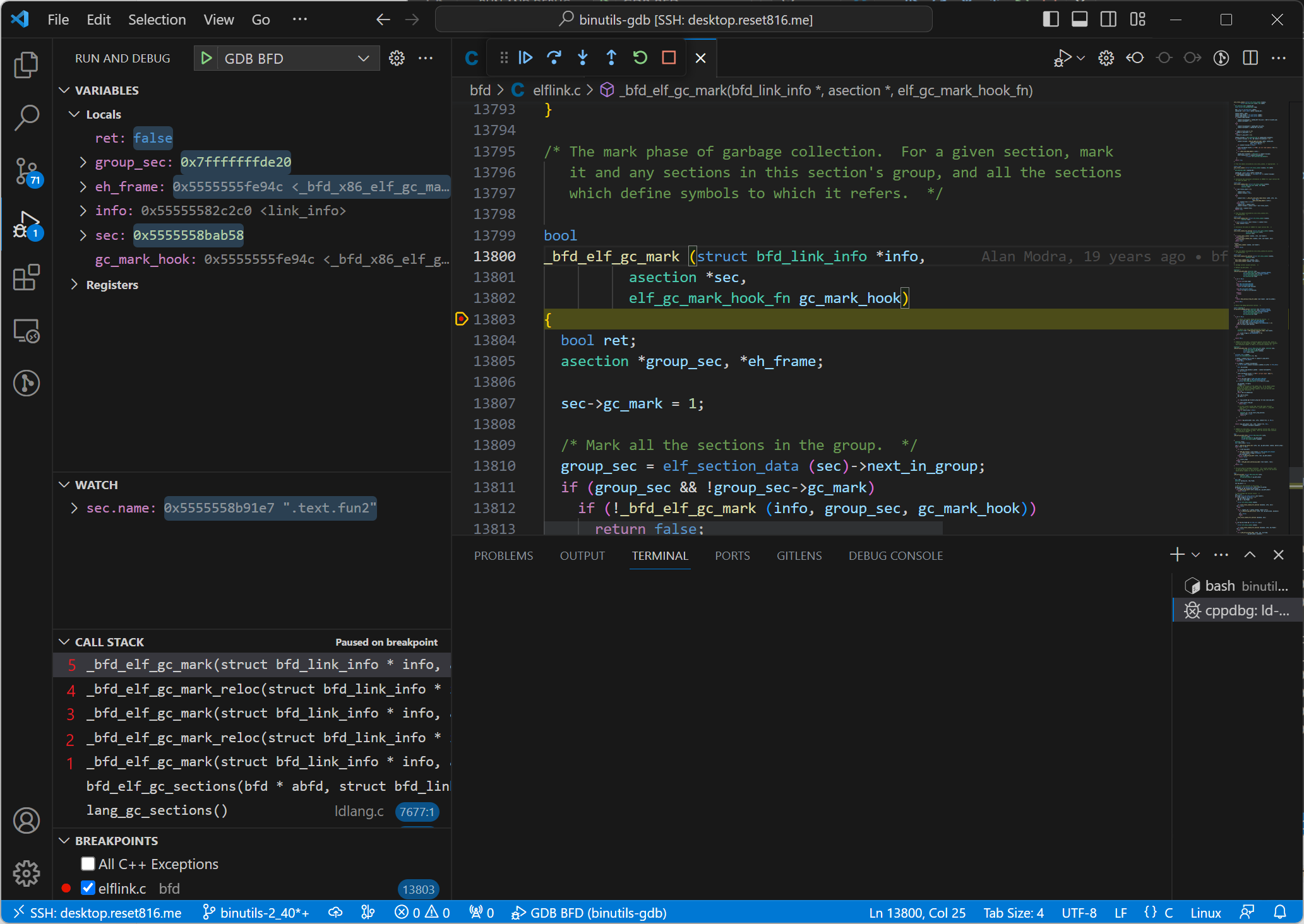
下表是重新建立 frame 5 后当前调用栈的状态。和之前表不同,此时 frame 5 的 sec.name 值为 .text.fun2。
frame | sec.name |
|---|---|
frame 5 | .text.fun2 |
frame 3 | .text.main |
frame 1 | .text |
据此可以推测出,这里是在递归扫描 section 引用到的其他 section,即扫描一个 section 时,会将当前 section 的 gc_mark 置为 1,然后遍历该 section 的引用(压入调用栈),直到栈空且 for 循环执行完毕,对该 section 的扫描才结束。
数据结构和代码解析
遍历当前 section 引用到的 section 是 _bfd_elf_gc_mark() 函数中的这段代码完成的:
for (; cookie.rel < cookie.relend; cookie.rel++)
if (!_bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc (info, sec, gc_mark_hook, &cookie))
{
ret = false;
break;
}
_bfd_elf_gc_mark() 函数会调用 _bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc() 函数
这里 cookie 的类型是 elf_reloc_cookie:
struct elf_reloc_cookie
{
Elf_Internal_Rela *rels, *rel, *relend; // 表示 ELF 文件中的重定位条目。分别表示重定位条目数组的开始、末尾,和当前处理的重定位条目
Elf_Internal_Sym *locsyms; // ELF 文件中的本地符号表。
bfd *abfd;
size_t locsymcount;
size_t extsymoff;
struct elf_link_hash_entry **sym_hashes;
int r_sym_shift;
bool bad_symtab;
};
那么这个循环的目的是遍历所有的重定位条目(从 cookie.rel 到 cookie.relend 之间的所有条目)。在每次循环中,都会调用 _bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc 函数对当前的重定位条目进行处理。
下表是处理到 .text.fun2 时,栈的情况:
frame | 调用函数 | 处理对象 |
|---|---|---|
frame 5 | _bfd_elf_gc_mark() | .text.fun2 |
frame 4 | _bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc() | .text.fun2 |
frame 3 | _bfd_elf_gc_mark() | .text.main |
frame 5 | _bfd_elf_gc_mark_reloc() | .text.main |
frame 1 | _bfd_elf_gc_mark() | .text |
ELF 中的重定位条目
经过上面的解析,我们可以知道链接器是通过重定位条目来得知一个 section 引用了哪些其他 section 的。重定位条目其实就存储在 ELF 文件中。
$readelf -r test.o
Relocation section '.rela.text.main' at offset 0x278 contains 2 entries:
Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend
00000000000a 000600000004 R_X86_64_PLT32 0000000000000000 fun1 - 4
000000000014 000700000004 R_X86_64_PLT32 0000000000000000 fun2 - 4
Relocation section '.rela.eh_frame' at offset 0x2a8 contains 4 entries:
Offset Info Type Sym. Value Sym. Name + Addend
000000000020 000200000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .text.fun1 + 0
000000000040 000300000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .text.fun2 + 0
000000000060 000400000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .text.un_used + 0
000000000080 000500000002 R_X86_64_PC32 0000000000000000 .text.main + 0
从这个命令的输出我们可以得到下表:
| Sym. Name | Offset 十六进制 | Offset 十进制 |
|---|---|---|
fun1 | 00000000000a | 10 |
fun2 | 000000000014 | 20 |
这和函数调用链分析中的值分别为 10 和 20 的 r_offset 相同,同时 .rela.text.main 的条目项没有 un_used。说明链接器就是读取的这部分信息来解析引用关系的。
总结
我们通过研究链接器链接一个简单程序的例子,从源码层面分析了开启 --gc-sections 选项后链接器是如何确定一个函数的 section 引用了哪些其他函数 section 的。
链接器会从 ELF 文件中的重定位条目中解析处理引用信息。
其实对于全局变量来说,链接器会做一样的操作。-fdata-sections 选项会把每个全局变量放入单独的 .bss section 中。假如 fun1() 使用了全局变量 used,那么在遍历 fun1() 的引用时就会解析 .bss.used section。
参考资料
- Tiny Linux Kernel Project: Section Garbage Collection Patchset
- 重定位 - 深入理解计算机系统(CSAPP)
- 符号和符号表 - 深入理解计算机系统(CSAPP)
猜你喜欢:
- 我要投稿:发表原创技术文章,收获福利、挚友与行业影响力
- 知识星球:独家 Linux 实战经验与技巧,订阅「Linux知识星球」
- 视频频道:泰晓学院,B 站,发布各类 Linux 视频课
- 开源小店:欢迎光临泰晓科技自营店,购物支持泰晓原创
- 技术交流:Linux 用户技术交流微信群,联系微信号:tinylab
| 支付宝打赏 ¥9.68元 | 微信打赏 ¥9.68元 | |
 |  请作者喝杯咖啡吧 |  |
Read Album:
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(六):PLIC 和 串口支持
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(五):BootLoader 和设备树
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(四):内存模型和 CPU 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(三):KVM 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(二):库的 RISC-V 适配


