[置顶] 泰晓 RISC-V 实验箱,配套 30+ 讲嵌入式 Linux 系统开发公开课
OpenSBI 固件代码分析(三): sbi_init.c
Corrector: TinyCorrect v0.2-rc1 - [spaces comments refs pangu] Author: groot gr00t@foxmail.com Date: 2023/08/25 Revisor: Falcon falcon@tinylab.org Project: RISC-V Linux 内核剖析 Proposal: RISC-V Linux 内核 SBI 调用技术分析 Sponsor: PLCT Lab, ISCAS
前言
上一篇文章带领大家阅读了 ./firmware/fw_base.S 中的代码,在最后的分析中发现调用了 sbi_init() 函数。这个函数接替了汇编代码,继续进行 OpenSBI 的初始化。下面我们将紧接着上篇文章的内容,进入到 lib/sbi_init.c 文件中继续探索 OpenSBI 的启动流程。
代码解析
coolboot & warmboot
这里的 coolboot 和 warmboot 并不是传统意义上的热启动和冷启动,所以经常会造成误解。
在 OpenSBI 的 issue 中,找到了以下对话:
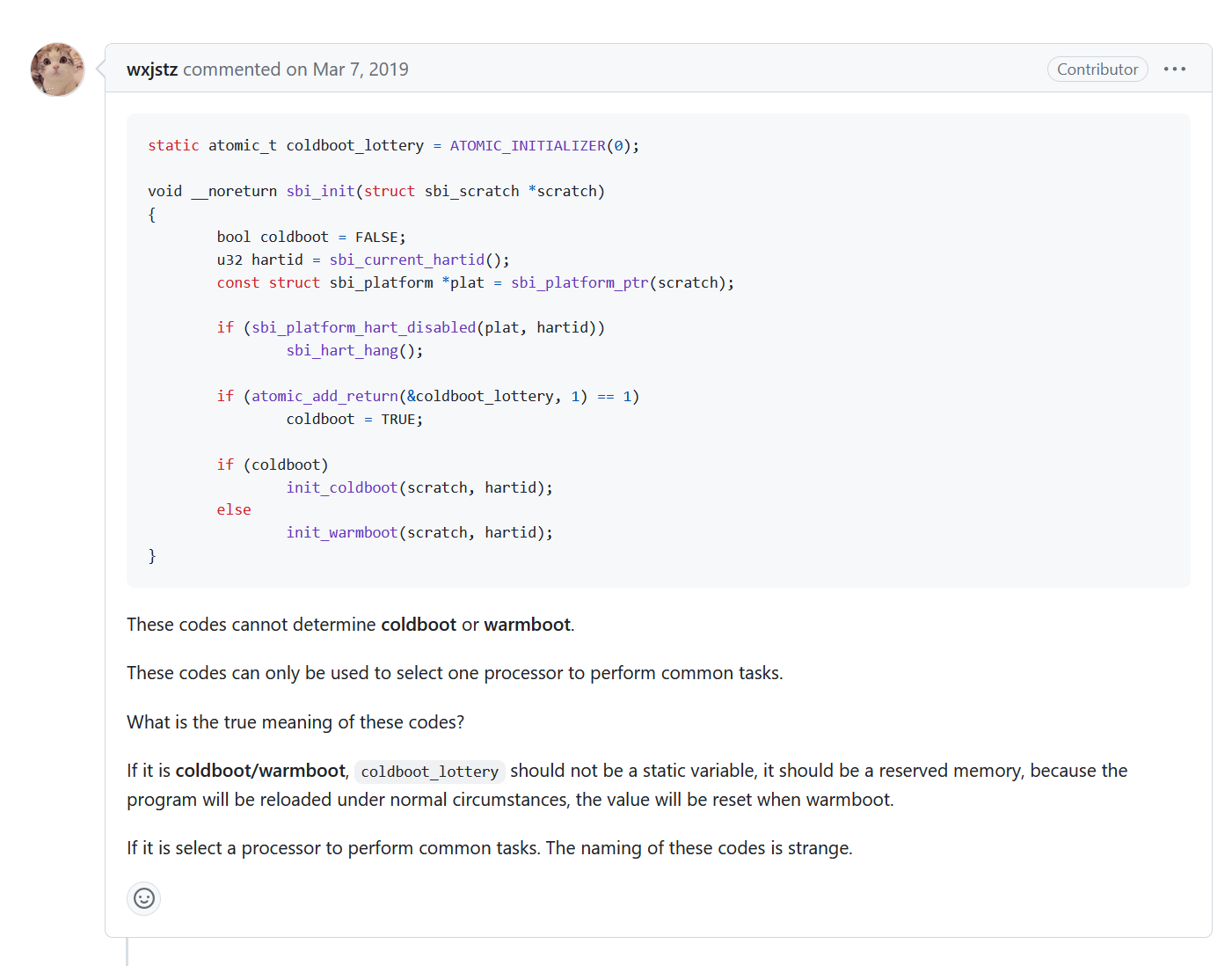
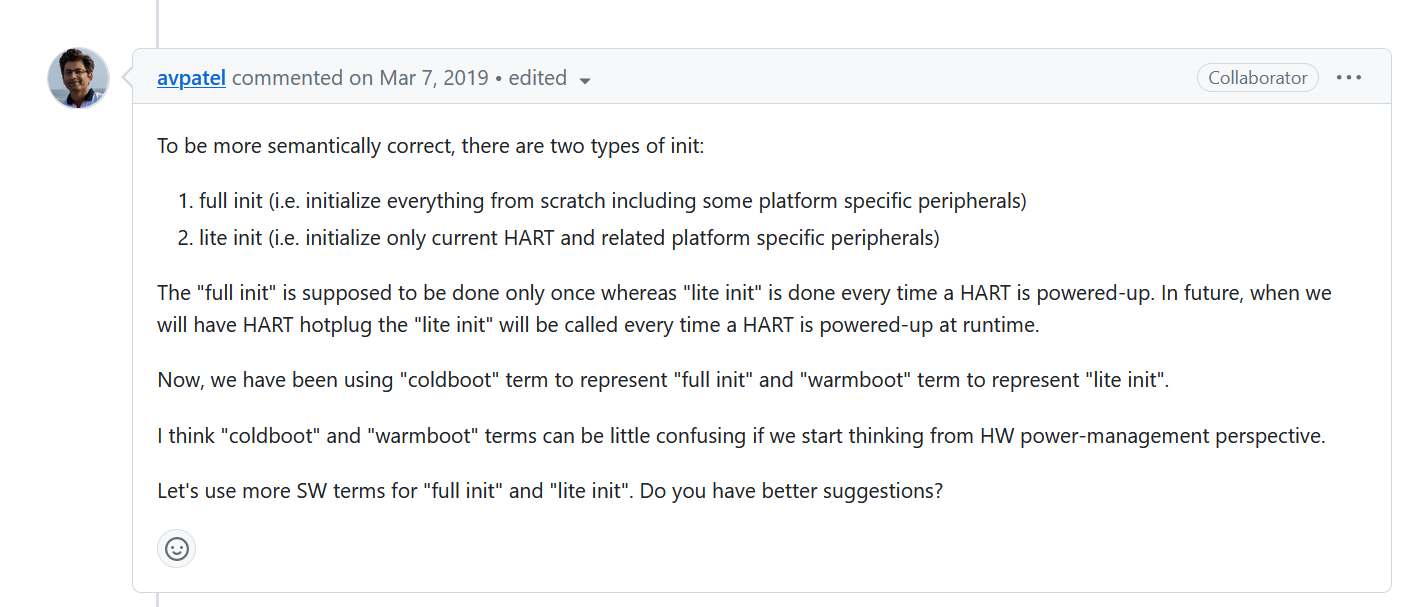
从这里的对话中我们可以清楚地得知,OpenSBI 中的 coolboot 和 warmboot 不代表传统意义上的热启动和冷启动。而是“完全初始化”和“部分初始化”的意思。
同时,对话中提出了要将 coolboot 和 warmboot 改名为 full_init 和 lite_init。 但是截止到目前(2023 年 8 月 25 日),仍没有进行修改······
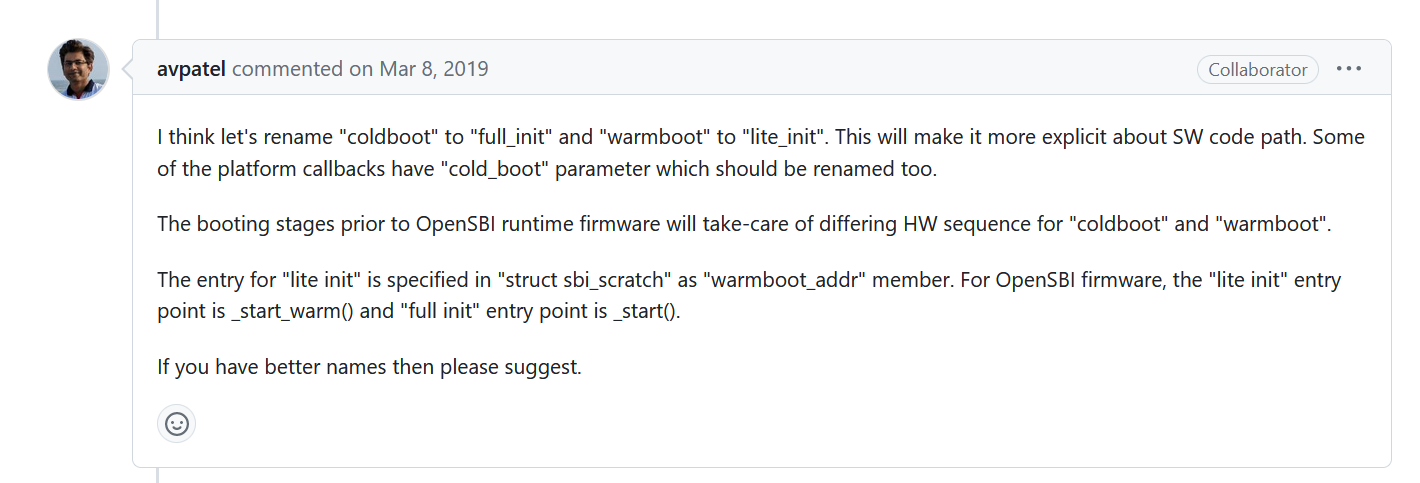
这里特此告知,避免大家产生误解。
sbi_init.c
代码的主要步骤如下:
- 检查当前 HART 的 ID 是否有效。如果 HART ID 超出了支持的最大范围,或者平台标记此 HART ID 为无效,函数将进入一个无限循环,即 HART 会进入挂起状态。
- 根据 scratch->next_mode 变量的值,检查当前 HART 是否支持下一个特权级。如果在 scratch->next_mode 指定的特权级(PRV_M、PRV_S、PRV_U)上,对应的扩展(S、U)在 misainstruction_set 字符串中被设置为支持,next_mode_supported 变量将被设置为 true。如果不支持,则函数将进入一个无限循环。
- 如果当前 HART 符合平台的冷启动条件(在 sbi_platform_cold_boot_allowed 函数中定义),且 next_mode_supported 为 true,并且通过原子交换将 coldboot_lottery 的值从 0 交换为 1 成功,则将 coldboot 设置为 true。(实际上这里永远是符合的,因为在该文件的第 507 行,coldboot_lottery 永远的被设置为 1)
- 执行硬件平台特定得非常早期的初始化操作,以便平台可以初始化特定于每个 HART 的控制和设备。如果初始化失败,函数将进入一个无限循环。
- 如果 coldboot 为 true,则调用 init_coldboot 函数执行冷启动初始化操作,否则调用 init_warmboot 函数执行热启动初始化操作。
// lib/sbi/sbi_init.c:521
void __noreturn sbi_init(struct sbi_scratch *scratch)
{
bool next_mode_supported = false;
bool coldboot = false;
u32 hartid = current_hartid();
const struct sbi_platform *plat = sbi_platform_ptr(scratch);
if ((SBI_HARTMASK_MAX_BITS <= hartid) ||
sbi_platform_hart_invalid(plat, hartid))
sbi_hart_hang();
switch (scratch->next_mode) {
case PRV_M:
next_mode_supported = true;
break;
case PRV_S:
if (misa_extension('S'))
next_mode_supported = true;
break;
case PRV_U:
if (misa_extension('U'))
next_mode_supported = true;
break;
default:
sbi_hart_hang();
}
/*
* Only the HART supporting privilege mode specified in the
* scratch->next_mode should be allowed to become the coldboot
* HART because the coldboot HART will be directly jumping to
* the next booting stage.
*
* We use a lottery mechanism to select coldboot HART among
* HARTs which satisfy above condition.
*/
if (sbi_platform_cold_boot_allowed(plat, hartid)) {
if (next_mode_supported &&
atomic_xchg(&coldboot_lottery, 1) == 0)
coldboot = true;
}
/*
* Do platform specific nascent (very early) initialization so
* that platform can initialize platform specific per-HART CSRs
* or per-HART devices.
*/
if (sbi_platform_nascent_init(plat))
sbi_hart_hang();
if (coldboot)
init_coldboot(scratch, hartid);
else
init_warmboot(scratch, hartid);
}
init_coolboot
在上面进行一些最基本处理之后,就开始进行 “full_init”,init_coldboot 函数会执行以下操作:
- 初始化 sbi_scratch 和堆内存
- 初始化域
- 分配和获取计数器的内存空间
- 初始化硬件组件,包括 HSM、平台、处理器、控制台和 PMU
- 打印启动横幅和信息
- 初始化中断控制器、IPI、TLB 和计时器
- 最终化域和平台
- 初始化异常调用
- 打印启动信息,包括通用信息、域信息和处理器信息
- 配置 PMP 以保护内存和设备访问权限
- 唤醒其他处于冷启动状态的处理器
- 完成 HSM 初始化和处理器启动
// lib/sbi/sbi_init.c:265
static void __noreturn init_coldboot(struct sbi_scratch *scratch, u32 hartid)
{
int rc;
unsigned long *count;
const struct sbi_platform *plat = sbi_platform_ptr(scratch);
/* Note: This has to be first thing in coldboot init sequence */
rc = sbi_scratch_init(scratch);
if (rc)
sbi_hart_hang();
/* Note: This has to be second thing in coldboot init sequence */
rc = sbi_heap_init(scratch);
if (rc)
sbi_hart_hang();
/* Note: This has to be the third thing in coldboot init sequence */
rc = sbi_domain_init(scratch, hartid);
if (rc)
sbi_hart_hang();
entry_count_offset = sbi_scratch_alloc_offset(__SIZEOF_POINTER__);
if (!entry_count_offset)
sbi_hart_hang();
init_count_offset = sbi_scratch_alloc_offset(__SIZEOF_POINTER__);
if (!init_count_offset)
sbi_hart_hang();
count = sbi_scratch_offset_ptr(scratch, entry_count_offset);
(*count)++;
rc = sbi_hsm_init(scratch, hartid, true);
if (rc)
sbi_hart_hang();
rc = sbi_platform_early_init(plat, true);
if (rc)
sbi_hart_hang();
rc = sbi_hart_init(scratch, true);
if (rc)
sbi_hart_hang();
rc = sbi_console_init(scratch);
if (rc)
sbi_hart_hang();
rc = sbi_pmu_init(scratch, true);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: pmu init failed (error %d)\n",
__func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
sbi_boot_print_banner(scratch);
rc = sbi_irqchip_init(scratch, true);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: irqchip init failed (error %d)\n",
__func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
rc = sbi_ipi_init(scratch, true);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: ipi init failed (error %d)\n", __func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
rc = sbi_tlb_init(scratch, true);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: tlb init failed (error %d)\n", __func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
rc = sbi_timer_init(scratch, true);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: timer init failed (error %d)\n", __func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
/*
* Note: Finalize domains after HSM initialization so that we
* can startup non-root domains.
* Note: Finalize domains before HART PMP configuration so
* that we use correct domain for configuring PMP.
*/
rc = sbi_domain_finalize(scratch, hartid);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: domain finalize failed (error %d)\n",
__func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
/*
* Note: Platform final initialization should be after finalizing
* domains so that it sees correct domain assignment and PMP
* configuration for FDT fixups.
*/
rc = sbi_platform_final_init(plat, true);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: platform final init failed (error %d)\n",
__func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
/*
* Note: Ecall initialization should be after platform final
* initialization so that all available platform devices are
* already registered.
*/
rc = sbi_ecall_init();
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: ecall init failed (error %d)\n", __func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
sbi_boot_print_general(scratch);
sbi_boot_print_domains(scratch);
sbi_boot_print_hart(scratch, hartid);
/*
* Configure PMP at last because if SMEPMP is detected,
* M-mode access to the S/U space will be rescinded.
*/
rc = sbi_hart_pmp_configure(scratch);
if (rc) {
sbi_printf("%s: PMP configure failed (error %d)\n",
__func__, rc);
sbi_hart_hang();
}
wake_coldboot_harts(scratch, hartid);
count = sbi_scratch_offset_ptr(scratch, init_count_offset);
(*count)++;
sbi_hsm_hart_start_finish(scratch, hartid);
}
如果在任何步骤中发生错误,处理器将进入死循环,指示启动失败。
这里不再到每一个函数内部给大家进行讲解,留在后面的文章再仔细介绍,只对 sbi_ecall_init 和 sbi_boot_print_general、sbi_boot_print_domains、sbi_boot_print_hart 这三个打印函数中所打印的内容进行说明,帮助读者理解。
sbi_boot_print_general
首先是一些硬件平台的基本信息
// lib/sbi/sbi_init.c:80
/* Platform details */
sbi_printf("Platform Name : %s\n",
sbi_platform_name(plat));
sbi_platform_get_features_str(plat, str, sizeof(str));
sbi_printf("Platform Features : %s\n", str);
sbi_printf("Platform HART Count : %u\n",
sbi_platform_hart_count(plat));
idev = sbi_ipi_get_device();
sbi_printf("Platform IPI Device : %s\n",
(idev) ? idev->name : "---");
tdev = sbi_timer_get_device();
sbi_printf("Platform Timer Device : %s @ %luHz\n",
(tdev) ? tdev->name : "---",
(tdev) ? tdev->timer_freq : 0);
cdev = sbi_console_get_device();
sbi_printf("Platform Console Device : %s\n",
(cdev) ? cdev->name : "---");
hdev = sbi_hsm_get_device();
sbi_printf("Platform HSM Device : %s\n",
(hdev) ? hdev->name : "---");
pdev = sbi_pmu_get_device();
sbi_printf("Platform PMU Device : %s\n",
(pdev) ? pdev->name : "---");
srdev = sbi_system_reset_get_device(SBI_SRST_RESET_TYPE_COLD_REBOOT, 0);
sbi_printf("Platform Reboot Device : %s\n",
(srdev) ? srdev->name : "---");
srdev = sbi_system_reset_get_device(SBI_SRST_RESET_TYPE_SHUTDOWN, 0);
sbi_printf("Platform Shutdown Device : %s\n",
(srdev) ? srdev->name : "---");
susp_dev = sbi_system_suspend_get_device();
sbi_printf("Platform Suspend Device : %s\n",
(susp_dev) ? susp_dev->name : "---");
cppc_dev = sbi_cppc_get_device();
sbi_printf("Platform CPPC Device : %s\n",
(cppc_dev) ? cppc_dev->name : "---");
反映在输出就是下图:
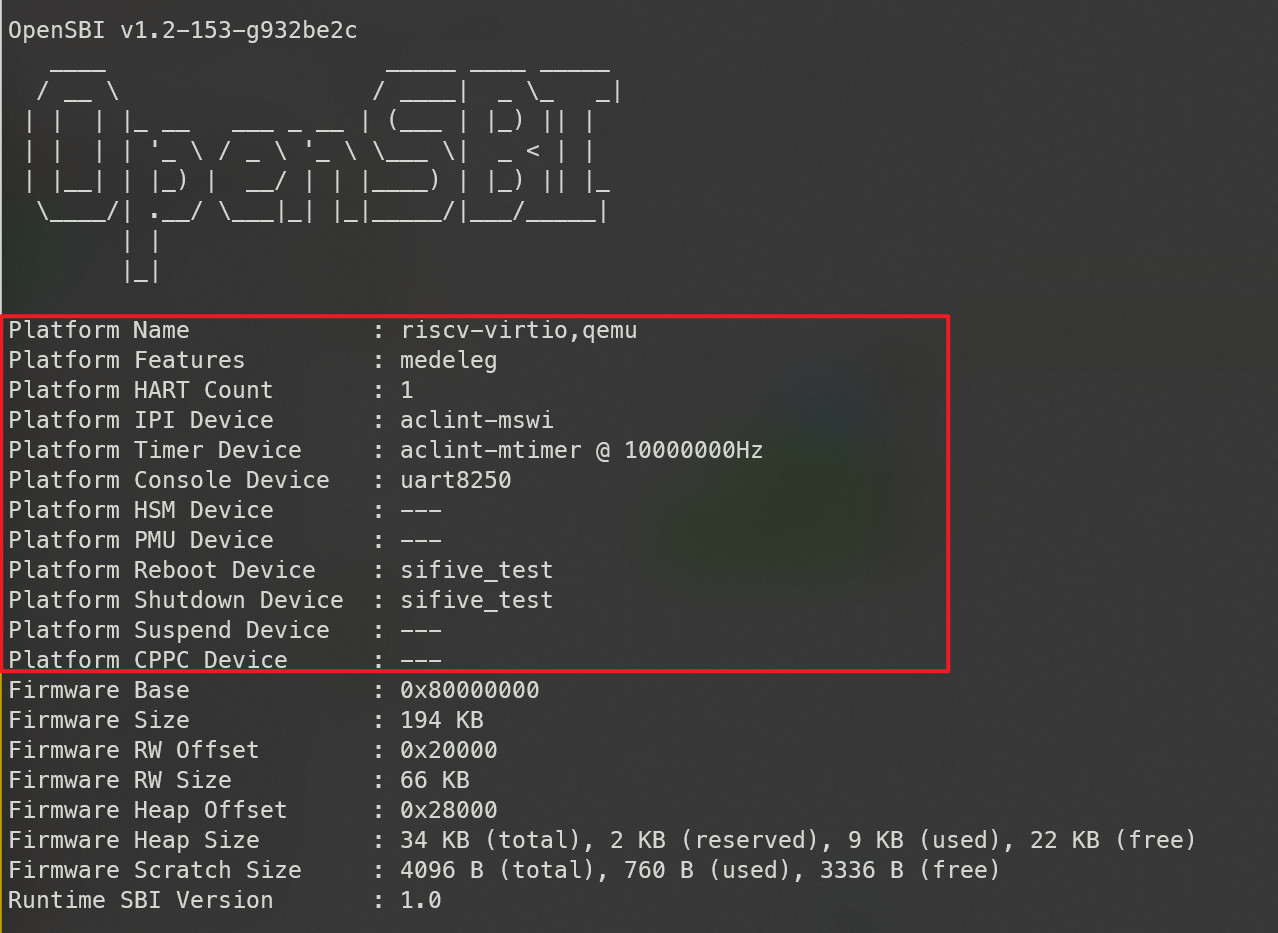
这里的输出主要是一些平台的外设信息。
之后就是一些固件信息和 SBI 版本信息
// lib/sbi/sbi_init.c:17
/* Firmware details */
sbi_printf("Firmware Base : 0x%lx\n", scratch->fw_start);
sbi_printf("Firmware Size : %d KB\n",
(u32)(scratch->fw_size / 1024));
sbi_printf("Firmware RW Offset : 0x%lx\n", scratch->fw_rw_offset);
sbi_printf("Firmware RW Size : %d KB\n",
(u32)((scratch->fw_size - scratch->fw_rw_offset) / 1024));
sbi_printf("Firmware Heap Offset : 0x%lx\n", scratch->fw_heap_offset);
sbi_printf("Firmware Heap Size : "
"%d KB (total), %d KB (reserved), %d KB (used), %d KB (free)\n",
(u32)(scratch->fw_heap_size / 1024),
(u32)(sbi_heap_reserved_space() / 1024),
(u32)(sbi_heap_used_space() / 1024),
(u32)(sbi_heap_free_space() / 1024));
sbi_printf("Firmware Scratch Size : "
"%d B (total), %d B (used), %d B (free)\n",
SBI_SCRATCH_SIZE,
(u32)sbi_scratch_used_space(),
(u32)(SBI_SCRATCH_SIZE - sbi_scratch_used_space()));
/* SBI details */
sbi_printf("Runtime SBI Version : %d.%d\n",
sbi_ecall_version_major(), sbi_ecall_version_minor());
sbi_printf("\n");
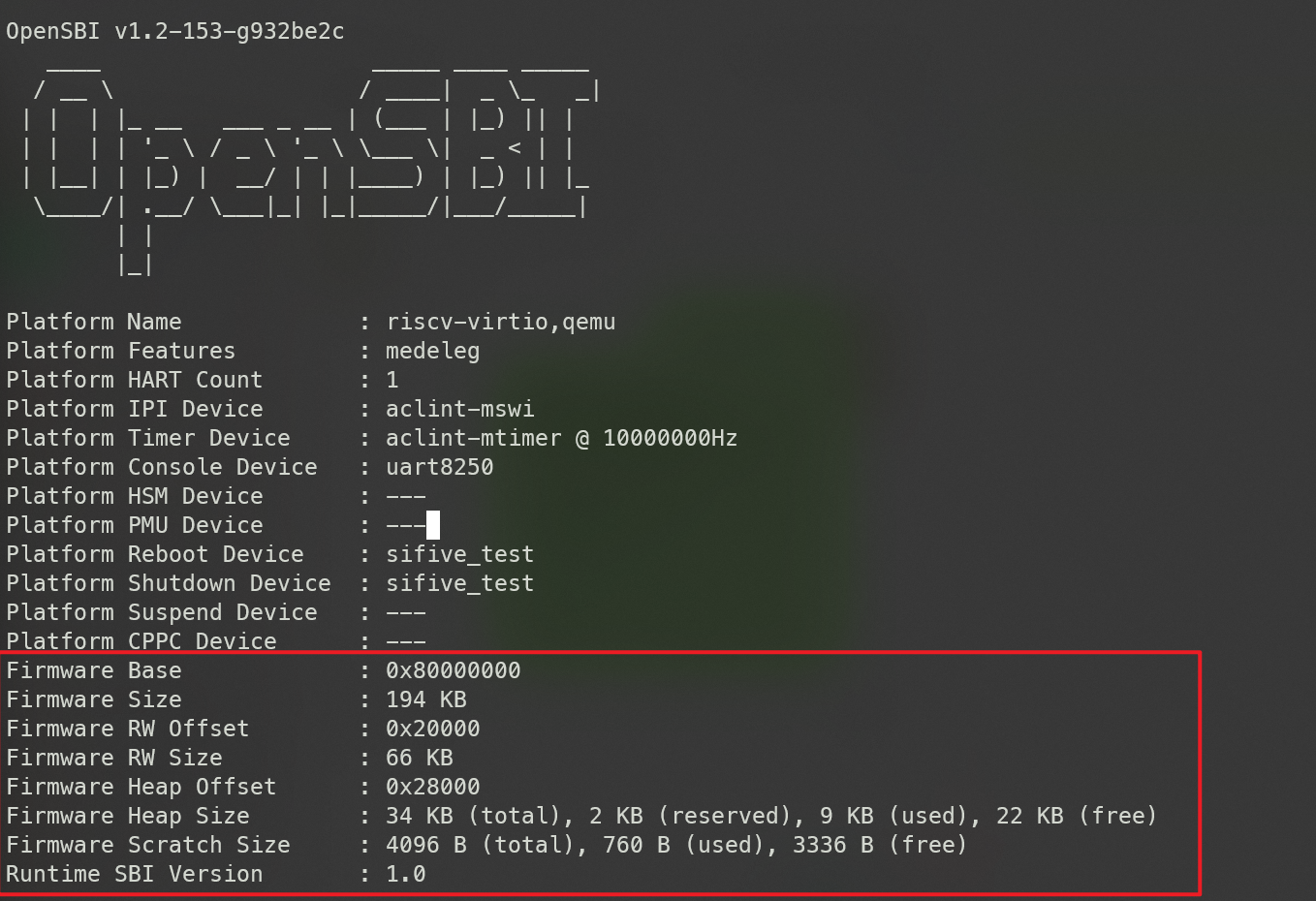
sbi_boot_print_domain
这一部分打印一些关于 OpenSBI domain 的信息:
lib/sbi/sbi_domain.c:407
sbi_printf("Domain%d Name %s: %s\n",
dom->index, suffix, dom->name);
sbi_printf("Domain%d Boot HART %s: %d\n",
dom->index, suffix, dom->boot_hartid);
k = 0;
sbi_printf("Domain%d HARTs %s: ", dom->index, suffix);
sbi_hartmask_for_each_hart(i, dom->possible_harts)
sbi_printf("%s%d%s", (k++) ? "," : "",
i, sbi_domain_is_assigned_hart(dom, i) ? "*" : "");
sbi_printf("\n");
i = 0;
sbi_domain_for_each_memregion(dom, reg) {
rstart = reg->base;
rend = (reg->order < __riscv_xlen) ?
rstart + ((1UL << reg->order) - 1) : -1UL;
sbi_printf("Domain%d Region%02d %s: 0x%" PRILX "-0x%" PRILX " ",
dom->index, i, suffix, rstart, rend);
k = 0;
sbi_printf("M: ");
if (reg->flags & SBI_DOMAIN_MEMREGION_MMIO)
sbi_printf("%cI", (k++) ? ',' : '(');
if (reg->flags & SBI_DOMAIN_MEMREGION_M_READABLE)
sbi_printf("%cR", (k++) ? ',' : '(');
if (reg->flags & SBI_DOMAIN_MEMREGION_M_WRITABLE)
sbi_printf("%cW", (k++) ? ',' : '(');
if (reg->flags & SBI_DOMAIN_MEMREGION_M_EXECUTABLE)
sbi_printf("%cX", (k++) ? ',' : '(');
sbi_printf("%s ", (k++) ? ")" : "()");
k = 0;
sbi_printf("S/U: ");
if (reg->flags & SBI_DOMAIN_MEMREGION_SU_READABLE)
sbi_printf("%cR", (k++) ? ',' : '(');
if (reg->flags & SBI_DOMAIN_MEMREGION_SU_WRITABLE)
sbi_printf("%cW", (k++) ? ',' : '(');
if (reg->flags & SBI_DOMAIN_MEMREGION_SU_EXECUTABLE)
sbi_printf("%cX", (k++) ? ',' : '(');
sbi_printf("%s\n", (k++) ? ")" : "()");
i++;
}
sbi_printf("Domain%d Next Address%s: 0x%" PRILX "\n",
dom->index, suffix, dom->next_addr);
sbi_printf("Domain%d Next Arg1 %s: 0x%" PRILX "\n",
dom->index, suffix, dom->next_arg1);
sbi_printf("Domain%d Next Mode %s: ", dom->index, suffix);
switch (dom->next_mode) {
case PRV_M:
sbi_printf("M-mode\n");
break;
case PRV_S:
sbi_printf("S-mode\n");
break;
case PRV_U:
sbi_printf("U-mode\n");
break;
default:
sbi_printf("Unknown\n");
break;
}
sbi_printf("Domain%d SysReset %s: %s\n",
dom->index, suffix, (dom->system_reset_allowed) ? "yes" : "no");
sbi_printf("Domain%d SysSuspend %s: %s\n",
dom->index, suffix, (dom->system_suspend_allowed) ? "yes" : "no");
因为这里没有注册新的域,默认的 HART 都被放在了 ROOT 域中。
ROOT 域是默认的 OpenSBI 域,它默认分配给 RISC-V 平台上所有的 HART。在引导过程的早期,OpenSBI 域支持将以下述方式手动构建 ROOT 域:
- index:ROOT 域的逻辑索引总是为零
- name:ROOT 域的名称为”root”
- assigned_harts:在引导时,所有有效的 RISC-V 平台 HART 都被分配为 ROOT 域,在之后根据 OpenSBI 平台支持而进行更改
- possible_harts:所有有效的 RISC-V 平台 HART 都可能成为 ROOT 域的 HART
- regions:ROOT 域拥有两个内存区域:
- 一个内存区域用于保护 OpenSBI 固件免受 S 模式和 U 模式的访问
- 一个内存区域为 order=__riscv_xlen,允许 S 模式和 U 模式访问完整的内存地址空间
- boot_hartid:冷启动的 HART 是启动 ROOT 域的 HART
- next_addr:冷启动 HART 临时空间中下一个引导阶段的地址是 ROOT 域的下一个地址
- next_arg1:冷启动 HART 临时空间中下一个引导阶段的参数 1 是 ROOT 域的下一个参数 1
- next_mode:冷启动 HART 临时空间中下一个引导阶段的模式是 ROOT 域的下一个模式
- system_reset_allowed:允许 ROOT 域重置系统
- system_suspend_allowed:允许 ROOT 域挂起系统
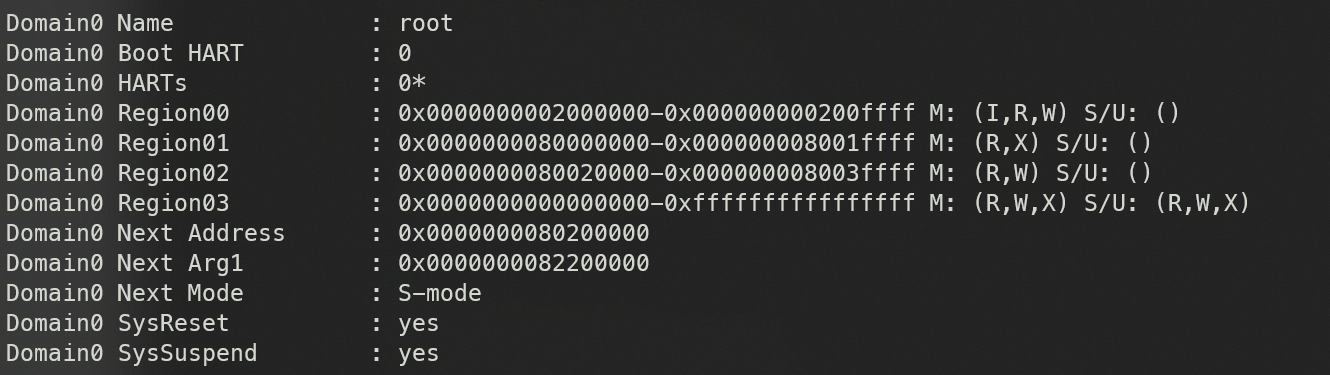
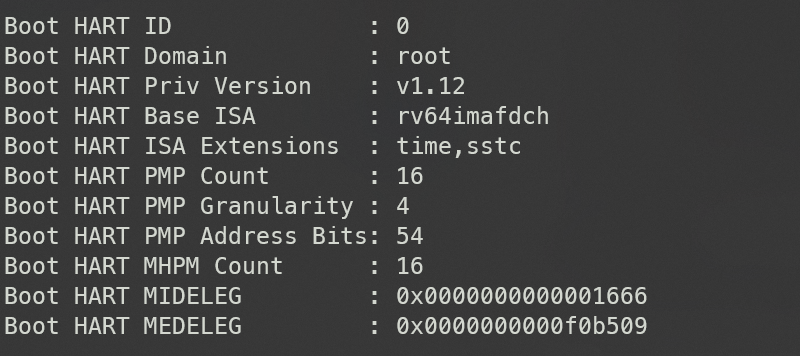
sbi_boot_print_hart
// lib/sbi/sbi_init.c:168
/* Boot HART details */
sbi_printf("Boot HART ID : %u\n", hartid);
sbi_printf("Boot HART Domain : %s\n", dom->name);
sbi_hart_get_priv_version_str(scratch, str, sizeof(str));
sbi_printf("Boot HART Priv Version : %s\n", str);
misa_string(xlen, str, sizeof(str));
sbi_printf("Boot HART Base ISA : %s\n", str);
sbi_hart_get_extensions_str(scratch, str, sizeof(str));
sbi_printf("Boot HART ISA Extensions : %s\n", str);
sbi_printf("Boot HART PMP Count : %d\n",
sbi_hart_pmp_count(scratch));
sbi_printf("Boot HART PMP Granularity : %lu\n",
sbi_hart_pmp_granularity(scratch));
sbi_printf("Boot HART PMP Address Bits: %d\n",
sbi_hart_pmp_addrbits(scratch));
sbi_printf("Boot HART MHPM Info : %lu (0x%08x)\n",
sbi_popcount(sbi_hart_mhpm_mask(scratch)),
sbi_hart_mhpm_mask(scratch));
sbi_hart_delegation_dump(scratch, "Boot HART ", " ");
这段代码打印了关于引导 HART(硬件线程)的详细信息,具体包括:
- “Boot HART ID”:引导 HART 的 ID。
- “Boot HART Domain”:引导 HART 的域名。
- “Boot HART Priv Version”:引导 HART 的特权版本。
- “Boot HART Base ISA”:引导 HART 的基本 ISA(指令集架构)。
- “Boot HART ISA Extensions”:引导 HART 的 ISA 扩展。
- “Boot HART PMP Count”:引导 HART 的 PMP(物理内存保护)计数。
- “Boot HART PMP Granularity”:引导 HART 的 PMP 粒度。
- “Boot HART PMP Address Bits”:引导 HART 的 PMP 地址位数。
- “Boot HART MHPM Info”:引导 HART 的 MHPM(硬件性能计数器)信息。
- “Boot HART “和” “:用作在前缀和对齐各个打印行的描述符。
以上这些信息可以用来显示引导 HART 的属性和配置信息。
小结
在这一节中我们介绍了进行到 sbi+init.c 文件中的一系列行为。为大家解答了 coolboot 和 warmboot 的真正含义。之后梳理了 coolboot 的基本流程,不过限于篇幅没有具体的讲每个函数的内容,之后会再进行补充。最后我们探求了 OpenSBI 启动过程中的输出,明确了各个输出的意义,方便大家能够在 OpenSBI 启动核的时候能够及时获取系统信息。
猜你喜欢:
- 我要投稿:发表原创技术文章,收获福利、挚友与行业影响力
- 知识星球:独家 Linux 实战经验与技巧,订阅「Linux知识星球」
- 视频频道:泰晓学院,B 站,发布各类 Linux 视频课
- 开源小店:欢迎光临泰晓科技自营店,购物支持泰晓原创
- 技术交流:Linux 用户技术交流微信群,联系微信号:tinylab
| 支付宝打赏 ¥9.68元 | 微信打赏 ¥9.68元 | |
 |  请作者喝杯咖啡吧 |  |
Read Album:
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(六):PLIC 和 串口支持
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(五):BootLoader 和设备树
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(四):内存模型和 CPU 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(三):KVM 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(二):库的 RISC-V 适配


