[置顶] 泰晓 RISC-V 实验箱,配套 30+ 讲嵌入式 Linux 系统开发公开课
RISC-V timer 在 Linux 中的实现
Author: Yu Liao yuliao0214@gmail.com Date: 2022/05/1 Revisor: lzufalcon falcon@tinylab.org Project: RISC-V Linux 内核剖析
RISC-V timer 相关寄存器
mtime & mtimecmp 寄存器
按照 RISC-V 定义,系统需要提供两个 64 位的 M 模式寄存器 mtime 和 mtimecmp,并通过 MMIO 方式映射到地址空间。
mtime 需要以固定的频率递增,并在发生溢出时回绕。当 mtime 大于或等于 mtimecmp 时,由核内中断控制器 (CLINT, Core-Local Interrupt Controller) 产生 timer 中断。中断的使能由 mie 寄存器中的 MTIE 和 STIE 位控制,mip 中的 MPIE 和 SPIE 则指示了 timer 中断是否处于 pending。在 RV32 中读取 mtimecmp 结果为低 32 位, mtimecmp 的高 32 位需要读取 mtimecmph 得到。
在 RISC-V 特权 ISA 规范 的 3.2.1 Machine Timer Registers (mtime and mtimecmp) 中详细介绍了这部分。
time CSR
RISC-V 还定义了一个 64 位非特权 CSR 寄存器 time,time 计数器是前面提到的 mtime 的只读映射。同样,在 RV32 中 timeh CSR 是 mtime 高 32 位的只读映射,对于 M 模式和 S 模式它们都是可读写的。
在 RISC-V 特权 ISA 规范 的 2.2 CSR Listing 和 3.1.11 Machine Counter-Enable Register (mcounteren) 可以找到这块的规范。
htimedelta & htimedeltah 寄存器
在增加虚拟化扩展以后,特权模式会发生一定变化,如下图(来源于参考文档 5)所示:
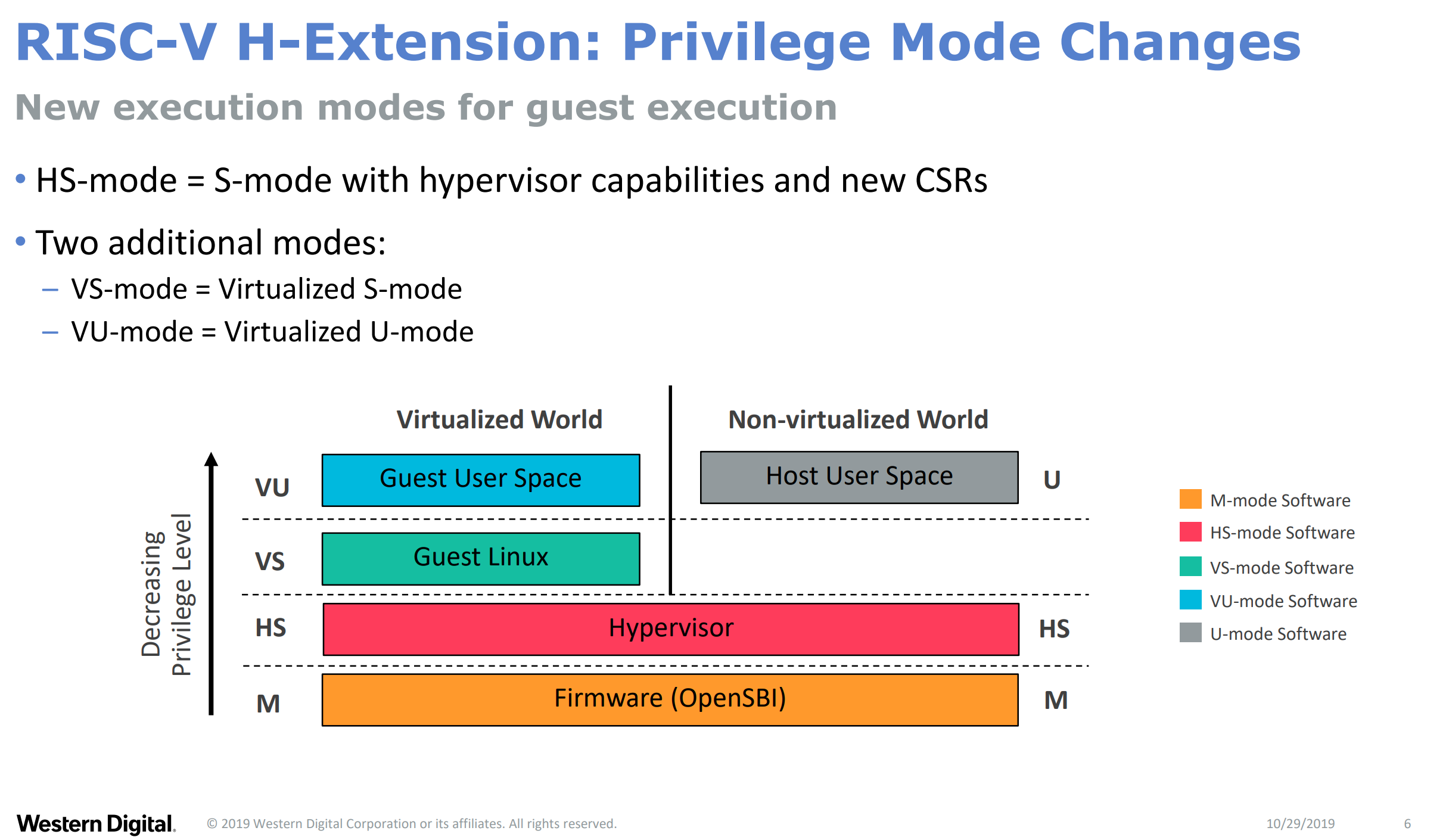
相应地,timer 支持也进行了如下扩展:
htimedelta 和 htimedeltah 是 Hypervisor 扩展里的 CSR,在 VS/VU 模式下读取 time 结果是真正的 host 中的 time 加上 htimedelta。同样的,对于 RV32 htimedelta 保存了低 32 位,高 32 位保存在 htimedeltah。
在 RISC-V 特权 ISA 规范 的 8.2.7 Hypervisor Time Delta Registers (htimedelta, htimedeltah) 中详细介绍了这部分。
Sstc 扩展
由于 mtimecmp 只能在 M 模式下访问,对于 S/HS 模式下的内核和 VU/VS 模式下的虚拟机需要通过 SBI 才能访问,会造成较大的中断延迟和性能开销。为了解决这一问题,RISC-V 新增了 Sstc 拓展支持(已批准但尚未最终集成到规范中)。
Sstc 扩展为 HS 模式和 VS 模式分别新增了 stimecmp 和 vstimecmp 寄存器,当 $time >= stimecmp$ (HS)或 $time+htimedelta >= vstimecmp$ (VS)时会产生 timer 中断,不再需要通过 SBI 陷入其他模式。
详见 RISC-V “stimecmp / vstimecmp” 扩展 。
Linux timer 实现
Linux 将底层时钟硬件抽象为两类设备:clockevent 和 clocksource,前者用来在未来指定的时间产生中断,通常用作定时器;后者则用于维护自系统启动以来所经过的时间。
当前 Linux 为 RISC-V 根据内核运行模式实现了两套驱动,代码路径为 drivers/clocksource/timer-riscv.c 和 drivers/clocksource/timer-clint.c。
本文代码基于最新的 Linux v5.18-rc4 和 OpenSBI v1.0,截止目前 Linux 对 Sstc 扩展的支持还没有合入主线内核,社区已有相关补丁:Add Sstc extension support。
mtime 频率由设备树 CPU 节点中的 timebase-frequency 定义,不同平台都各不相同,如 Kendryte K210 的频率是 7.8 MHz,平头哥 C910 的频率是 3 MHz,SiFive Unmatched A00 频率为 1 MHz。
NoMMU timer-clint.c
timer-clint.c 驱动适用于 NoMMU 系统,内核运行在 M 模式下,通过 CONFIG_CLINT_TIMER 使能该驱动。RV64 下 clocksource 是通过直接读取 mtime 寄存器实现的,RV32 系统需要分两次读取,并需要考虑产生进位的情况。
#ifdef CONFIG_64BIT
static u64 notrace clint_get_cycles64(void)
{
return clint_get_cycles();
}
#else /* CONFIG_64BIT */
static u64 notrace clint_get_cycles64(void)
{
u32 hi, lo;
do {
hi = clint_get_cycles_hi();
lo = clint_get_cycles();
} while (hi != clint_get_cycles_hi());
return ((u64)hi << 32) | lo;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_64BIT */
clint_get_cycles/clint_get_cycles_hi 直接通过内存访问寄存器。
#ifdef CONFIG_64BIT
#define clint_get_cycles() readq_relaxed(clint_timer_val)
#else
#define clint_get_cycles() readl_relaxed(clint_timer_val)
#define clint_get_cycles_hi() readl_relaxed(((u32 *)clint_timer_val) + 1)
#endif
clockevent 是通过使能 mie 的 TIMER 中断,并向 mtimecmp 寄存器写入期望的计数值实现的。
static int clint_clock_next_event(unsigned long delta,
struct clock_event_device *ce)
{
void __iomem *r = clint_timer_cmp +
cpuid_to_hartid_map(smp_processor_id());
csr_set(CSR_IE, IE_TIE);
writeq_relaxed(clint_get_cycles64() + delta, r);
return 0;
}
MMU timer-riscv.c
timer-riscv.c 驱动适用于有 MMU 的场景,内核运行在 S/HS 模式下,通过 CONFIG_RISCV_TIMER 可以使能该驱动。和 timer-riscv.c 的驱动相比,本质上也是访问 mtime 和 mtimecmp 寄存器,不过由于 S 模式下无法直接访问它们,需要通过其他方式间接完成。
RV64 的 clocksource 是通过 csrr 直接读取 time 寄存器实现的;在 RV32 系统由于一条指令无法读完,需要分两次读取 time 和 timeh, 并考虑可能发生进位的情况。前面提到 time 和 timeh 这两个 CSR 是 mtime 寄存器的映射,因此频率与精度和 mtime 是一致的。
#ifdef CONFIG_64BIT
static inline u64 get_cycles64(void)
{
return get_cycles();
}
#else /* CONFIG_64BIT */
static inline u64 get_cycles64(void)
{
u32 hi, lo;
do {
hi = get_cycles_hi();
lo = get_cycles();
} while (hi != get_cycles_hi());
return ((u64)hi << 32) | lo;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_64BIT */
static inline cycles_t get_cycles(void)
{
return csr_read(CSR_TIME);
}
static inline u32 get_cycles_hi(void)
{
return csr_read(CSR_TIMEH);
}
clockevent 则是通过 SBI 间接访问 mtimecmp 实现的。
static int riscv_clock_next_event(unsigned long delta,
struct clock_event_device *ce)
{
csr_set(CSR_IE, IE_TIE);
sbi_set_timer(get_cycles64() + delta);
return 0;
}
这里以 OpenSBI 来分析,如果不支持 Sstc 扩展则调用在 SBI 中注册的 timer_event_start 函数写入 mtimecmp,这个需要具体平台自己去实现。
void sbi_timer_event_start(u64 next_event)
{
sbi_pmu_ctr_incr_fw(SBI_PMU_FW_SET_TIMER);
/**
* Update the stimecmp directly if available. This allows
* the older software to leverage sstc extension on newer hardware.
*/
if (sbi_hart_has_feature(sbi_scratch_thishart_ptr(), SBI_HART_HAS_SSTC)) {
#if __riscv_xlen == 32
csr_write(CSR_STIMECMP, next_event & 0xFFFFFFFF);
csr_write(CSR_STIMECMPH, next_event >> 32);
#else
csr_write(CSR_STIMECMP, next_event);
#endif
} else if (timer_dev && timer_dev->timer_event_start) {
timer_dev->timer_event_start(next_event);
csr_clear(CSR_MIP, MIP_STIP);
}
csr_set(CSR_MIE, MIP_MTIP);
}
在支持 Sstc 扩展后,可以直接访问 stimecmp 寄存器,避免通过 SBI 调用的方式产生的开销。社区已开展相关工作:RISC-V: Prefer sstc extension if available。
KVM vcpu_timer.c
在 VS 模式下读取 time 时,KVM 会返回真正的 time 加上 htimedelta。
static u64 kvm_riscv_current_cycles(struct kvm_guest_timer *gt)
{
return get_cycles64() + gt->time_delta;
}
在 VS 模式下设置 mtimecmp 时,KVM 会开启一个已经创建好的高精度定时器,并把定时器的到期时间设置为写入 mtimecmp 值对应的 ns。
int kvm_riscv_vcpu_timer_next_event(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, u64 ncycles)
{
struct kvm_vcpu_timer *t = &vcpu->arch.timer;
struct kvm_guest_timer *gt = &vcpu->kvm->arch.timer;
u64 delta_ns;
if (!t->init_done)
return -EINVAL;
kvm_riscv_vcpu_unset_interrupt(vcpu, IRQ_VS_TIMER);
delta_ns = kvm_riscv_delta_cycles2ns(ncycles, gt, t);
t->next_cycles = ncycles;
hrtimer_start(&t->hrt, ktime_set(0, delta_ns), HRTIMER_MODE_REL);
t->next_set = true;
return 0;
}
在定时器到期后,KVM 会为 Guest 产生 TIMER 中断。
static enum hrtimer_restart kvm_riscv_vcpu_hrtimer_expired(struct hrtimer *h)
{
u64 delta_ns;
struct kvm_vcpu_timer *t = container_of(h, struct kvm_vcpu_timer, hrt);
struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu = container_of(t, struct kvm_vcpu, arch.timer);
struct kvm_guest_timer *gt = &vcpu->kvm->arch.timer;
if (kvm_riscv_current_cycles(gt) < t->next_cycles) {
delta_ns = kvm_rizscv_delta_cycles2ns(t->next_cycles, gt, t);
hrtimer_forward_now(&t->hrt, ktime_set(0, delta_ns));
return HRTIMER_RESTART;
}
t->next_set = false;
kvm_riscv_vcpu_set_interrupt(vcpu, IRQ_VS_TIMER);
return HRTIMER_NORESTART;
}
因此 VS 模式设置时钟事件需要通过 SBI 调用进入 HS 模式然后再进入 M 模式,会产生较大的开销。同样,在支持 Sstc 扩展后,可以直接访问 vstimecmp 并产生 timer 中断,社区目前已经开展了相关的工作:RISC-V: KVM: Support sstc extension。
参考文档
- RISC-V Platform
- RISC-V ISA Specification
- RISC-V “stimecmp / vstimecmp” Extension
- 基于 FPGA 与 RISC-V 的嵌入式系统设计
- RISC-V虚拟化扩展
猜你喜欢:
- 我要投稿:发表原创技术文章,收获福利、挚友与行业影响力
- 知识星球:独家 Linux 实战经验与技巧,订阅「Linux知识星球」
- 视频频道:泰晓学院,B 站,发布各类 Linux 视频课
- 开源小店:欢迎光临泰晓科技自营店,购物支持泰晓原创
- 技术交流:Linux 用户技术交流微信群,联系微信号:tinylab
| 支付宝打赏 ¥9.68元 | 微信打赏 ¥9.68元 | |
 |  请作者喝杯咖啡吧 |  |
Read Album:
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(六):PLIC 和 串口支持
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(五):BootLoader 和设备树
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(四):内存模型和 CPU 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(三):KVM 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(二):库的 RISC-V 适配


