[置顶] 泰晓 RISC-V 实验箱,配套 30+ 讲嵌入式 Linux 系统开发公开课
Linux 的 RISC-V 拓展支持与 alternative 运行时代码段修改
Corrector: TinyCorrect v0.2-rc1 - [spaces codeinline pangu] Author: Tan Yuan tanyuan@tinylab.org Date: 20230730 Revisor: Falcon falcon@tinylab.org Project: RISC-V Linux 内核剖析 Proposal: 通过编译器解决因链接过程 KEEP 操作引起的 Section GC 失败问题 Sponsor: PLCT Lab, ISCAS
概述
RISC-V 拥有许多拓展指令集,CPU 可以选择性地支持这些拓展指令集。其中,RISC-V ISA Zbb 是一种基本位操作拓展指令集,可应用于字符串相关操作。近期,Linux 内核开始采用 Zbb 中的新指令来优化字符串操作,从而提升系统性能。
然而,内核必须同时考虑不支持 Zbb 的设备。使用不同的函数实现可能会引起多个问题,包括:
- 如果 CPU 不支持新指令该如何处理?
- 如何将旧指令实现的函数替换成新指令实现的函数?
- 启动的最初阶段内核不知道 CPU 支持哪些拓展。
为了解决这些问题,内核采用了”alternative”功能来实现函数替换。该功能可以在内核运行时将原有代码内容动态替换为新的代码内容,修改代码段以更改函数的执行路径。
“alternative”根据 CPU 的型号来决定是否替代代码。如果 CPU 不支持 Zbb,那么在内核启动时,就不会更改函数的执行路径,避免运行到 Zbb 专属指令的部分。
接下来,我们将研究 Linux Kernel v6.5-rc2 如何将原有的 strcmp 替换为 Zbb 中的新指令,并详细阐述”alternative”的实现原理。
准备工作
我们需要准备好测试环境,包括支持 Zbb 的工具链、支持 Zbb 的 CPU、并开启内核关于 Zbb 的选项。
工具链支持和内核选项
在内核代码中搜索 Zbb,可以找到如下配置选项:
// arch/riscv/Kconfig:507
config TOOLCHAIN_HAS_ZBB
bool
default y
depends on !64BIT || $(cc-option,-mabi=lp64 -march=rv64ima_zbb)
depends on !32BIT || $(cc-option,-mabi=ilp32 -march=rv32ima_zbb)
depends on LLD_VERSION >= 150000 || LD_VERSION >= 23900
depends on AS_HAS_OPTION_ARCH
config RISCV_ISA_ZBB
bool "Zbb extension support for bit manipulation instructions"
depends on TOOLCHAIN_HAS_ZBB
depends on MMU
depends on RISCV_ALTERNATIVE
default y
help
Adds support to dynamically detect the presence of the ZBB
extension (basic bit manipulation) and enable its usage.
The Zbb extension provides instructions to accelerate a number
of bit-specific operations (count bit population, sign extending,
bitrotation, etc).
If you don't know what to do here, say Y.
我们需要开启这两个选项。RISCV_ISA_ZBB 依赖于 TOOLCHAIN_HAS_ZBB,TOOLCHAIN_HAS_ZBB 需要 LD_VERSION >= 23900。
我们可以使用 Binutils 2.40。如果发行版仓库中 Binutils 低于该版本,可以在 交叉编译工具链镜像 上下载该版本的 Binutils。
在正确的环境变量配置下,我们可以打开 menuconfig 来开启 RISCV_ISA_ZBB 选项。可以使用 / 来搜索选项,并且使用数字 1、2 来快速跳转到目标选项位置。
make ARCH=riscv CROSS_COMPILE=riscv64-linux- menuconfig
QEMU 支持
我们需要使用支持 Zbb 的 CPU 来运行内核。
QEMU 关于这方面的文档并不完整。通过在其 代码 中搜索,发现 v8.1.0-rc1 版本中的 veyron-v1 CPU 支持 Zbb。
使用 QEMU 运行 Linux Kernel:
qemu-system-riscv64 \
-nographic \
-machine virt \
-cpu veyron-v1 \
-kernel arch/riscv/boot/Image \
-append "console=ttyS0"
如果我们想使用不支持 Zbb 的 CPU 来调试,可以使用 sifive-u54 CPU。
qemu-system-riscv64 \
-nographic \
-machine virt \
-cpu sifive-u54 \
-kernel arch/riscv/boot/Image \
-append "console=ttyS0"
调试配置
内核开启调试选项
需要开启内核中的 CONFIG_DEBUG_INFO_DWARF_TOOLCHAIN_DEFAULT 选项来为内核增加调试信息。
VSCode 调试配置
我们可以使用 VSCode 来让调试更加便利。
只需要在项目根目录下创建两个文件 .vscode/launch.json 和 .vscode/tasks.json,即可使用 VSCode 来调试内核。
// .vscode/launch.json
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Kernel Debug",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"miDebuggerServerAddress": "localhost:1234",
"program": "${workspaceFolder:}/vmlinux",
"sourceFileMap": {
"kernel.map": "${workspaceFolder:}/System.map"
},
"MIMode": "gdb",
"externalConsole": false,
"miDebuggerPath": "gdb-multiarch",
"internalConsoleOptions": "openOnSessionStart",
"preLaunchTask": "qemu-debug",
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder:}",
"setupCommands": [
{
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"description": "Enable GDB pretty printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
},
{
"text": "set architecture riscv:rv64",
"description": "Set target architecture",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"miDebuggerArgs": "-q"
}
]
}
// .vscode/tasks.json
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "qemu-debug",
"command": "echo starting qemu... 1>&2 && qemu-system-riscv64 -nographic -machine virt -cpu veyron-v1 -kernel arch/riscv/boot/Image -append console=ttyS0 -s -S",
"isBackground": true,
"presentation": {
"echo": true,
"reveal": "always",
"focus": true,
"panel": "shared",
"showReuseMessage": false
},
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder:}"
},
"problemMatcher": {
"pattern": {
"regexp": "."
},
"background": {
"activeOnStart": true,
"beginsPattern": ".",
"endsPattern": "."
}
}
}
]
}
通过更改 .vscode/tasks.json 中的 command 项,可以修改 QEMU 的参数。
创建好这两个文件后,即可使用 VSCode 调试功能。
alternative 原理
动态替换代码
首先我们来看一下 arch/riscv/lib/strcmp.S,可以 在线 查看代码。
strcmp.S 的结构为:
strcmp:
ALTERNATIVE("nop", "j strcmp_zbb", 0, RISCV_ISA_EXT_Zbb, CONFIG_RISCV_ISA_ZBB)
< 通用的 strcmp 汇编代码 >
ret
strcmp_zbb:
< 使用 Zbb 拓展指令的 strcmp 汇编代码 >
ret
ALTERNATIVE 是 汇编宏,在汇编转换为机器码的阶段展开。编译后,这部分代码段在运行时实际上会变为:
strcmp:
nop
< 通用的 strcmp 汇编代码 >
ret
strcmp_zbb:
< 使用 Zbb 拓展指令的 strcmp 汇编代码 >
ret
原来的 ALTERNATIVE 展开成 nop 指令。
我们可以推测,在内核启动时,如果 CPU 支持并且内核配置了 ZBB 选项,ALTERNATIVE 将把 nop 指令修改为跳转指令,跳转到 strcmp_zbb 处执行;相反,不支持 ZBB 的 CPU 或者没有配置 ZBB 选项,只会执行通用的 strcmp 汇编代码。
运行时的代码段修改
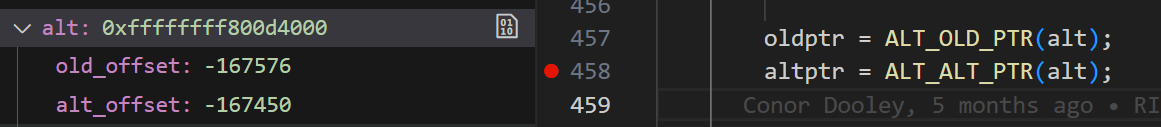
先在 arch/riscv/kernel/alternative.c 的 riscv_alternative_fix_offsets() 函数打断点。
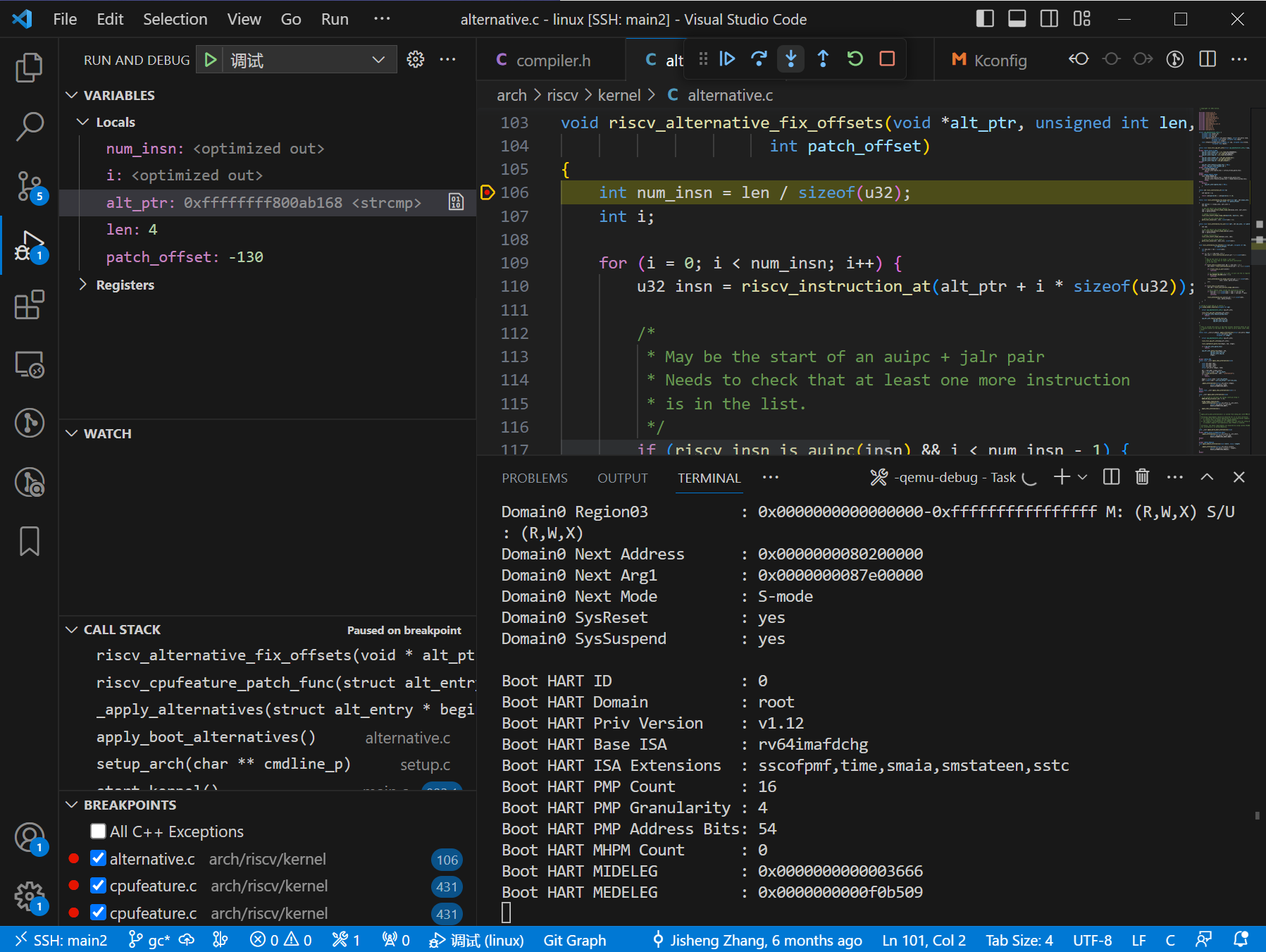
这里的 alt_ptr 是 strcmp,有点像我们要找的地方。我们又在调用栈的上一层 riscv_cpufeature_patch_func() 打断点并重新运行,看执行 riscv_alternative_fix_offsets() 函数之前是什么样子。
调用栈的更上一层,即 riscv_alternative_fix_offsets() 的调用者 _apply_alternatives() 函数我们暂时不讨论。
我们暂停在执行 riscv_cpufeature_patch_func() 函数的 patch_text_nosync() 语句前:
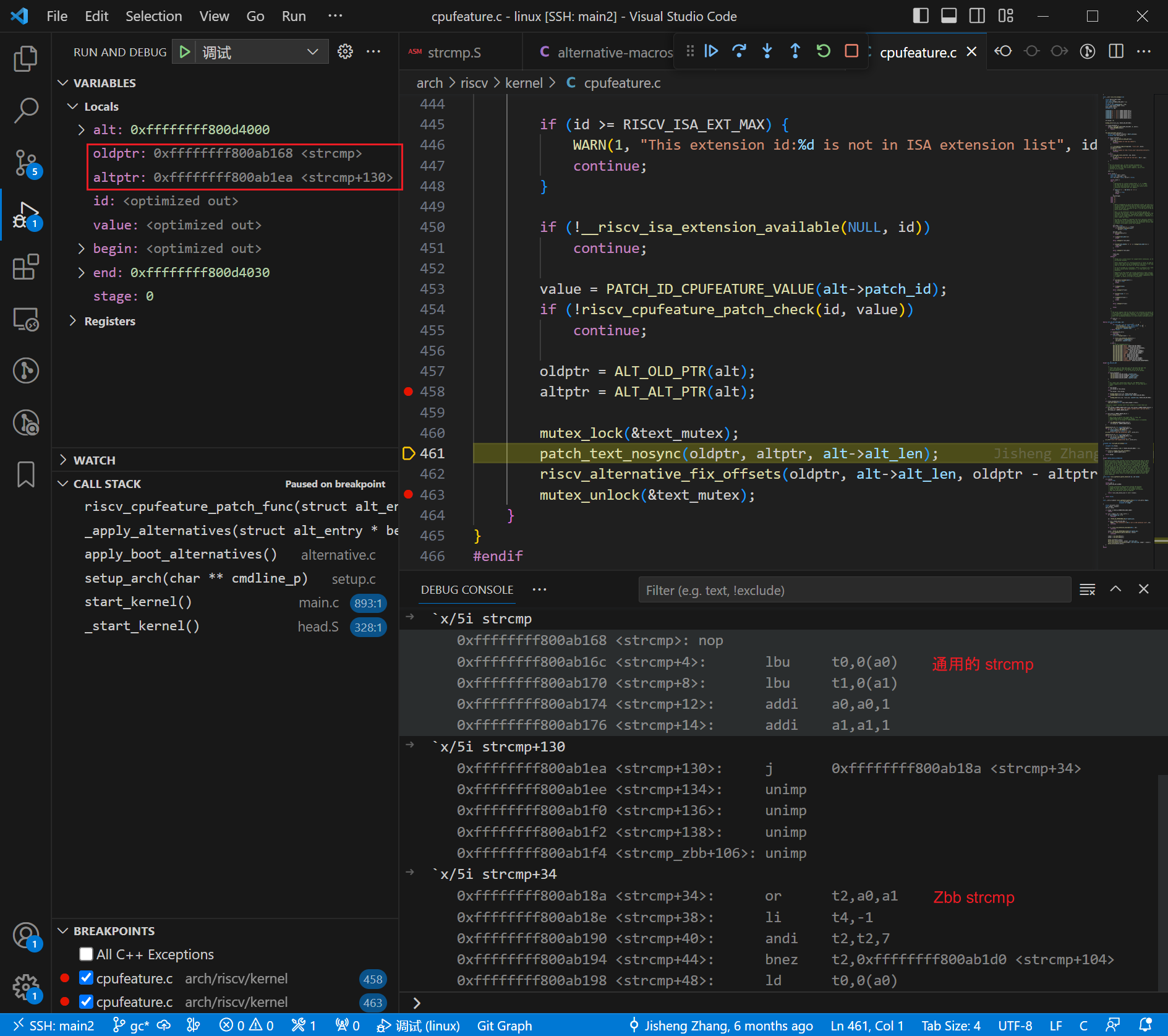
oldptr 指向代码段 strcmp,altptr 指向代码段 strcmp+130,strcmp+130 的指令内容为 j strcmp+34,即跳转到 Zbb 拓展实现的 strcmp_zbb 处。
为什么突然出现 strcmp+130 这样的地址呢?
刚刚的 strcmp.S 代码中是这样的:
ALTERNATIVE("nop", "j strcmp_zbb", 0, RISCV_ISA_EXT_ZBB, CONFIG_RISCV_ISA_ZBB)
我们对 vmlinux 进行反汇编。strcmp+130 是整个的 strcmp.S 的结束地址,再往后是 strlen,
$ riscv64-linux-objdump -D -j .text vmlinux | grep -A "35" "<strcmp_zbb>:"
ffffffff800ab18a <strcmp_zbb>:
ffffffff800ab18a: 00b563b3 or t2,a0,a1
ffffffff800ab18e: 5efd li t4,-1
ffffffff800ab190: 0073f393 and t2,t2,7
ffffffff800ab194: 02039e63 bnez t2,ffffffff800ab1d0 <strcmp_zbb+0x46>
ffffffff800ab198: 00053283 ld t0,0(a0)
ffffffff800ab19c: 0005b303 ld t1,0(a1)
ffffffff800ab1a0: 2872de13 orc.b t3,t0
ffffffff800ab1a4: 03de1163 bne t3,t4,ffffffff800ab1c6 <strcmp_zbb+0x3c>
ffffffff800ab1a8: 0521 add a0,a0,8
ffffffff800ab1aa: 05a1 add a1,a1,8
ffffffff800ab1ac: fe6286e3 beq t0,t1,ffffffff800ab198 <strcmp_zbb+0xe>
ffffffff800ab1b0: 6b82d293 rev8 t0,t0
ffffffff800ab1b4: 6b835313 rev8 t1,t1
ffffffff800ab1b8: 0062b533 sltu a0,t0,t1
ffffffff800ab1bc: 40a00533 neg a0,a0
ffffffff800ab1c0: 00156513 or a0,a0,1
ffffffff800ab1c4: 8082 ret
ffffffff800ab1c6: 00629563 bne t0,t1,ffffffff800ab1d0 <strcmp_zbb+0x46>
ffffffff800ab1ca: 4501 li a0,0
ffffffff800ab1cc: 8082 ret
ffffffff800ab1ce: 0001 nop
ffffffff800ab1d0: 00054283 lbu t0,0(a0)
ffffffff800ab1d4: 0005c303 lbu t1,0(a1)
ffffffff800ab1d8: 0505 add a0,a0,1
ffffffff800ab1da: 0585 add a1,a1,1
ffffffff800ab1dc: 00629463 bne t0,t1,ffffffff800ab1e4 <strcmp_zbb+0x5a>
ffffffff800ab1e0: fe0298e3 bnez t0,ffffffff800ab1d0 <strcmp_zbb+0x46>
ffffffff800ab1e4: 40628533 sub a0,t0,t1
ffffffff800ab1e8: 8082 ret
ffffffff800ab1ea: fa1ff06f j ffffffff800ab18a <strcmp_zbb>
...
ffffffff800ab1f8 <__pi_strlen>:
ffffffff800ab1f8: 00000013 nop
ffffffff800ab1fc: 832a mv t1,a0
可以发现新指令 j strcmp_zbb 实际上是存放在 strcmp.S 的结束处的。说明 ALTERNATIVE 搞了一些魔法,定位到了该节的末尾,插入了新代码 j strcmp_zbb。我们将在文章的下个小节讨论这个魔法。
继续分析后续代码。在执行了 patch_text_nosync() 后,刚刚查看的 strcmp 内存处的 nop 指令已经变成了 j 0xffffffff800ab108,如下图:
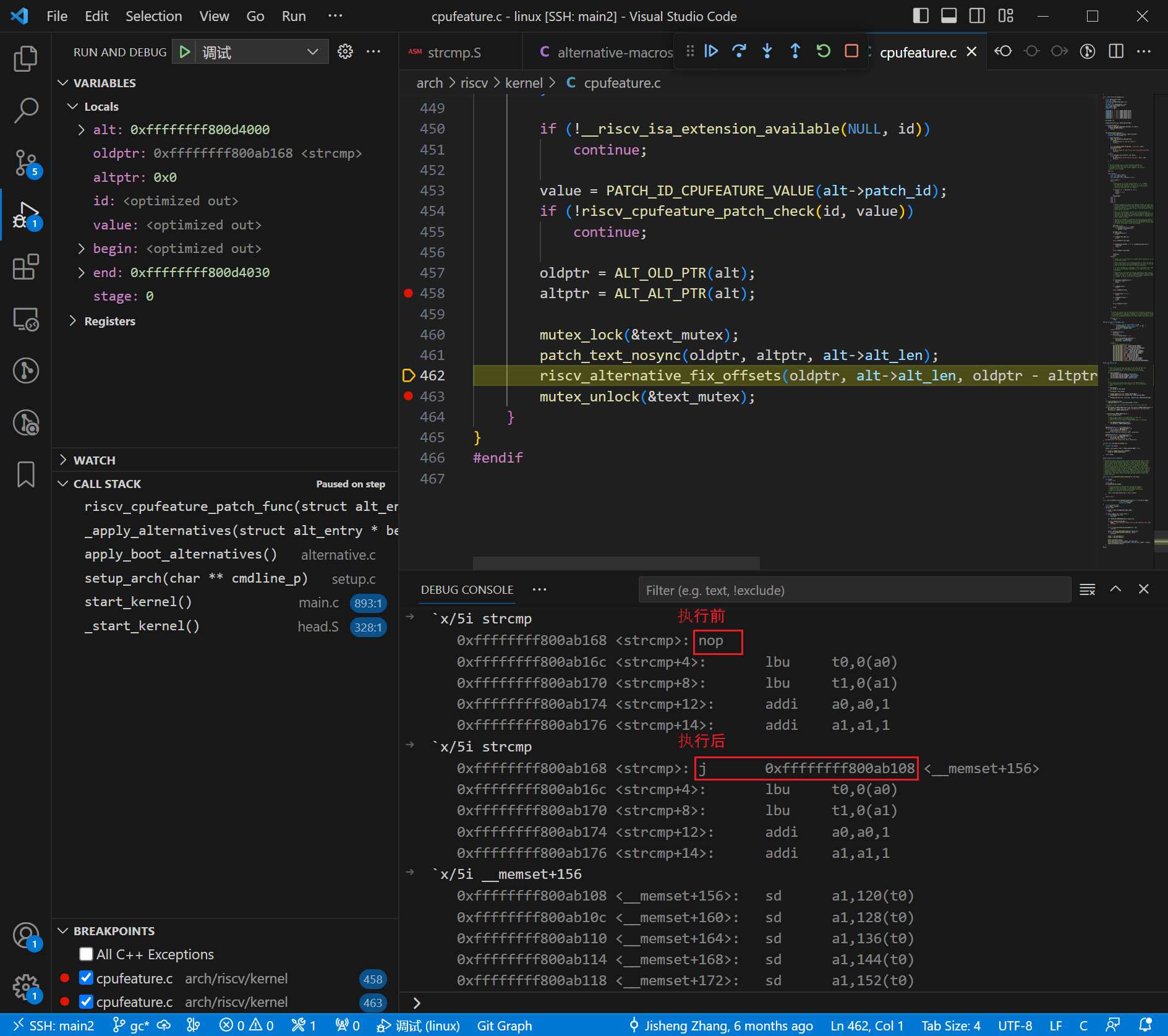
这个跳转地址很奇怪,看起来没有任何作用。我们将在文章的下个小节讨论它。
执行了 riscv_alternative_fix_offsets() 后,原来的 nop 变成了 j strcmp+34。
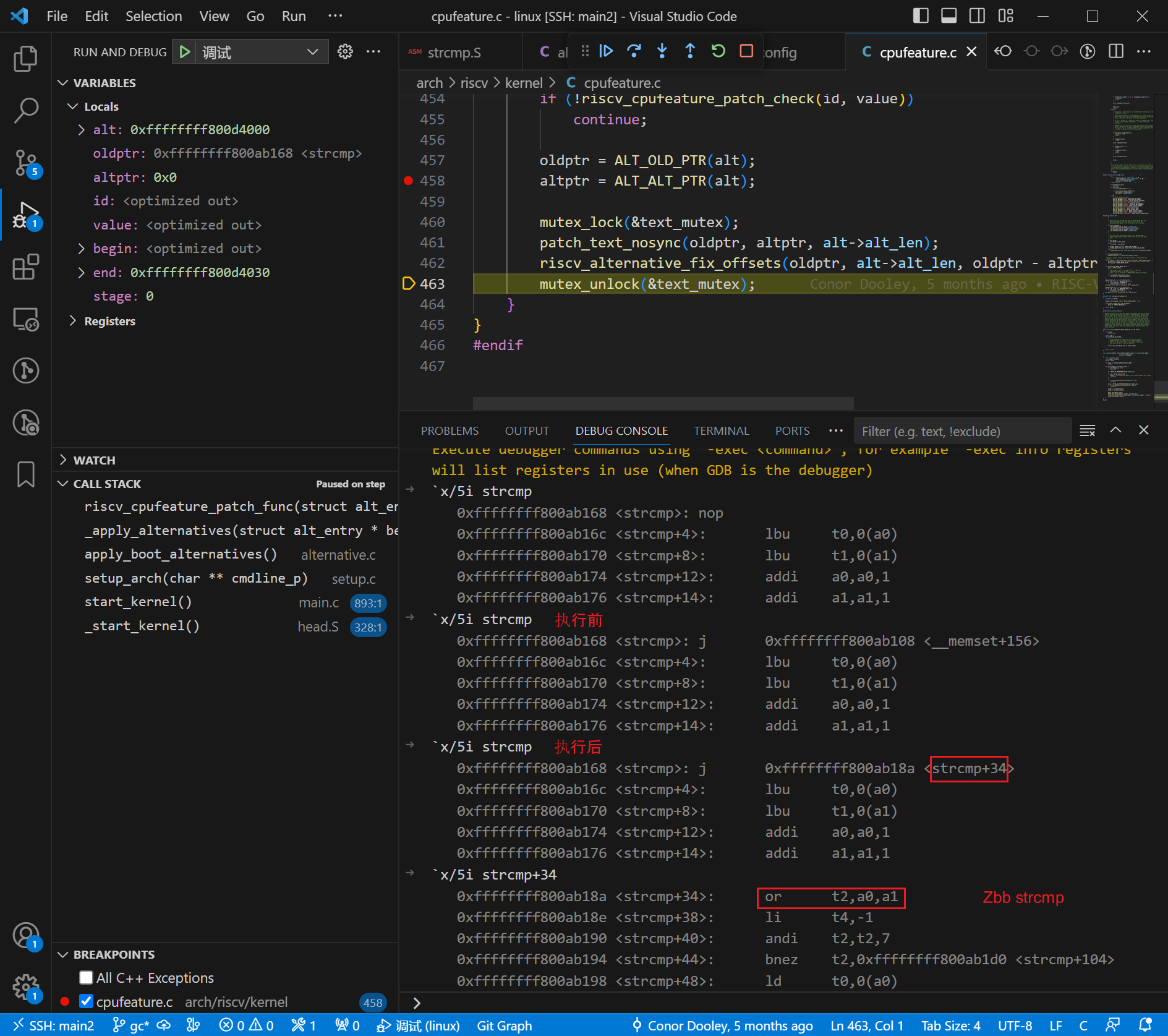
查看 strcmp+34 处的指令,可以发现该处即为使用 Zbb 拓展指令实现的高性能 strcmp_zbb。
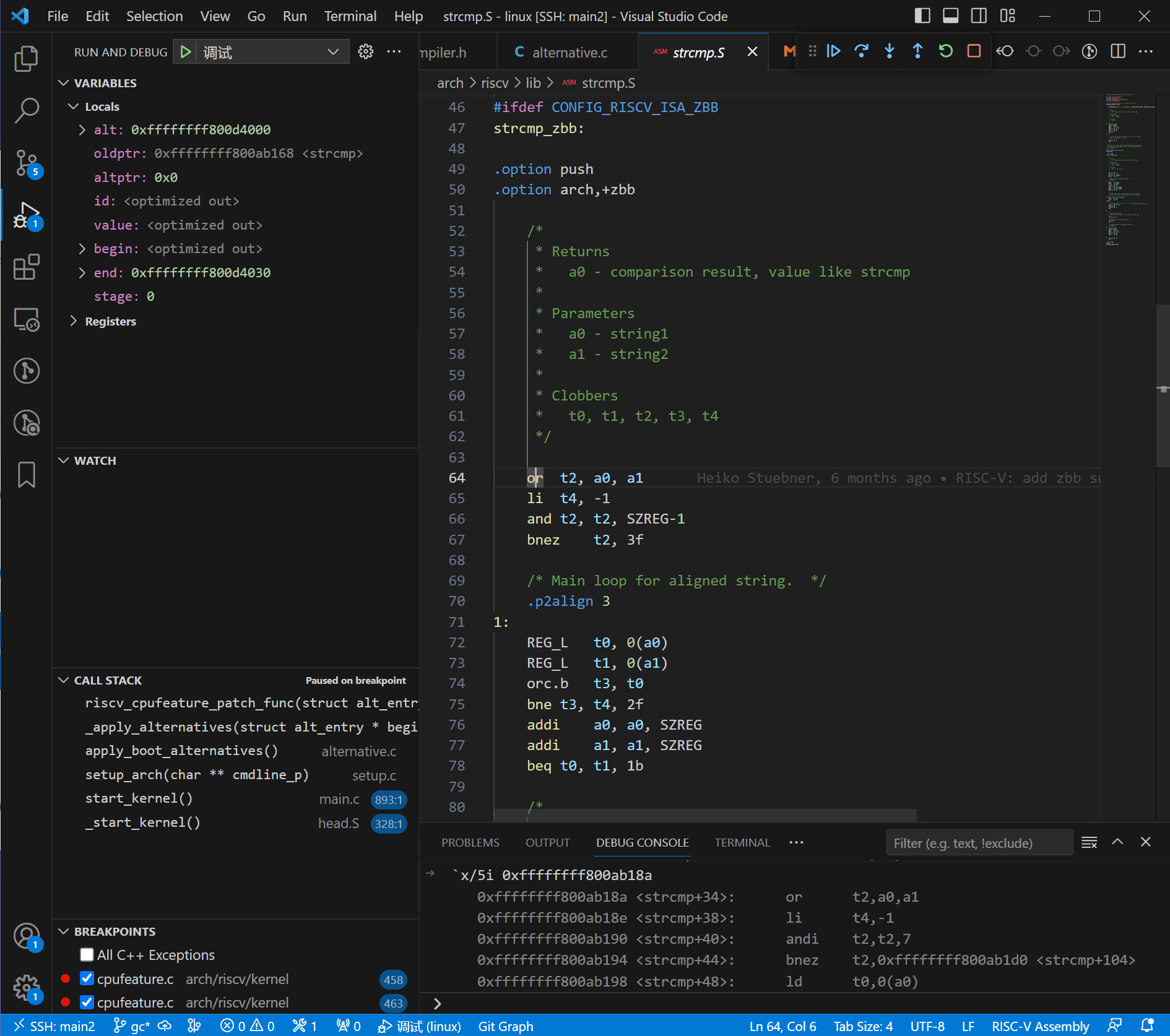
在此之后,内核代码段的内容已经被修改。原本调用 strcmp() 执行的第一条指令为 nop 指令,现在 nop 指令被修改为无条件跳转指令。调用 strcmp() 会立即跳转到 34 字节外的新指令 strcmp_zbb 上。
原有的:
strcmp:
nop
< 通用的 strcmp 汇编代码 >
ret
strcmp_zbb:
< 使用 Zbb 拓展指令的 strcmp_zbb 汇编代码 >
ret
修改后:
strcmp:
j strcmp_zbb
< 通用的 strcmp 汇编代码 >
ret
strcmp_zbb:
< 使用 Zbb 拓展指令的 strcmp_zbb 汇编代码 >
ret
代码段 strcmp label 处的指令的变化过程:
| 语句 | 代码段 strcmp label 处的指令 |
|---|---|
patch_text_nosync() 执行前 | nop |
patch_text_nosync() 执行后 | j 0xffffffff800ab108 <__memset+156> |
riscv_alternative_fix_offsets() 执行后 | j 0xffffffff800ab18a <strcmp+34> |
经过两次代码段修改,nop 指令被修改为跳转到 strcmp_zbb 的指令
ELF 的 .alternative 节与魔法
$ riscv64-linux-readelf -S vmlinux.o | grep -A 1 alternative
[21332] .alternative PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0017df18
0000000000000030 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
ALTERNATIVE 汇编宏展开时,会调用 ALT_NEW_CONTENT 汇编宏。
// arch/riscv/include/asm/alternative-macros.h:61
#define ALT_ENTRY(oldptr, newptr, vendor_id, patch_id, newlen) \
".4byte ((" oldptr ") - .) \n" \
".4byte ((" newptr ") - .) \n" \
".2byte " vendor_id "\n" \
".2byte " newlen "\n" \
".4byte " patch_id "\n"
#define ALT_NEW_CONTENT(vendor_id, patch_id, enable, new_c) \
".if " __stringify(enable) " == 1\n" \
".pushsection .alternative, \"a\"\n" \
ALT_ENTRY("886b", "888f", __stringify(vendor_id), __stringify(patch_id), "889f - 888f") \
".popsection\n" \
".subsection 1\n" \
"888 :\n" \
".option push\n" \
".option norvc\n" \
".option norelax\n" \
new_c "\n" \
".option pop\n" \
"889 :\n" \
".org . - (887b - 886b) + (889b - 888b)\n" \
".org . - (889b - 888b) + (887b - 886b)\n" \
".previous\n" \
".endif\n"
其中,".4byte ((" oldptr ") -.) \n" 将 oldptr label 到当前位置的距离存储到了这个 4byte 大小空间中。有了偏移量,在应用 alternative 时(即刚刚打断点的 riscv_cpufeature_patch_func() 函数的调用者 _apply_alternatives()),就能计算出新代码和旧代码的位置:
保存 offset 这个行为是由 该 patch 提供的,在这之前是直接保存的绝对地址,占用了更多的空间。
该汇编宏使用 .pushsection 在 ELF 文件中建立了 .alternative 节,将偏移量、vendor_id 和 patch_id 一起放在该节中。新代码并没有存储在这里,应该是为了缓存命中率的考虑,把新代码放在了所属代码节末尾。
存在于代码最前端的 ALTERNATIVE 展开后,能够把新代码放到代码段末尾,是通过 .subsection 和 .previous 实现的。
因此,后续 _apply_alternatives() 可以遍历该节每个 entry 来替换旧代码。
替换了两次旧代码?
在刚刚的分析中,我们 strcmp 处的代码被替换了两次,第一次替换的新代码跳转到 __memset+156 处,在 riscv_alternative_fix_offsets() 执行后,新代码才跳转到 strcmp_zbb 处。
首先我们来看看 patch_text_nosync() 的定义:
// arch/riscv/kernel/patch.c:99
int patch_text_nosync(void *addr, const void *insns, size_t len)
{
u32 *tp = addr;
int ret;
ret = patch_insn_write(tp, insns, len);
if (!ret)
flush_icache_range((uintptr_t) tp, (uintptr_t) tp + len);
return ret;
}
这个函数在 addr 上写入长度为 len 的 insns。更改代码段需要刷新 icache 来确保缓存一致性。
// arch/riscv/kernel/alternative.c:103
void riscv_alternative_fix_offsets(void *alt_ptr, unsigned int len,
int patch_offset)
{
int num_insn = len / sizeof(u32);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_insn; i++) {
u32 insn = riscv_instruction_at(alt_ptr + i * sizeof(u32));
/*
* May be the start of an auipc + jalr pair
* Needs to check that at least one more instruction
* is in the list.
*/
if (riscv_insn_is_auipc(insn) && i < num_insn - 1) {
u32 insn2 = riscv_instruction_at(alt_ptr + (i + 1) * sizeof(u32));
if (!riscv_insn_is_jalr(insn2))
continue;
/* if instruction pair is a call, it will use the ra register */
if (RV_EXTRACT_RD_REG(insn) != 1)
continue;
riscv_alternative_fix_auipc_jalr(alt_ptr + i * sizeof(u32),
insn, insn2, patch_offset);
i++;
}
if (riscv_insn_is_jal(insn)) {
s32 imm = riscv_insn_extract_jtype_imm(insn);
/* Don't modify jumps inside the alternative block */
if ((alt_ptr + i * sizeof(u32) + imm) >= alt_ptr &&
(alt_ptr + i * sizeof(u32) + imm) < (alt_ptr + len))
continue;
riscv_alternative_fix_jal(alt_ptr + i * sizeof(u32),
insn, patch_offset);
}
}
}
riscv_alternative_fix_offset() 函数根据偏移量计算出真正需要跳转的距离,按情况指派给 riscv_alternative_fix_auipc_jalr()、riscv_alternative_fix_jal()、riscv_alternative_fix_offsets() 函数,这些函数生成对应的指令后,再次使用 patch_text_nosync() 来修改目标地址代码。
经过 git blame 和搜索邮件列表,我们发现有一 patch 做了以下改动:
patch_text_nosync(alt->old_ptr, alt->alt_ptr, alt->alt_len);
+ riscv_alternative_fix_offsets(alt->old_ptr, alt->alt_len,
+ alt->old_ptr - alt->alt_ptr);
邮件中写到:
Alternatives live in a different section, so addresses used by call
functions will point to wrong locations after the patch got applied.
Similar to arm64, adjust the location to consider that offset.
原来是因为单独的一行 patch_text_nosync() 会有 bug,offset 计算不正确,所以才使用一个单独的函数来修补错误。
总结
内核的启动过程中,会检测 CPU 的型号,遍历 .alternative 节中的 entry,符合条件的 patch 会被 apply。apply 会修改目标地址的旧代码为新代码,同时确保 icache 一致性。
针对 RISC-V 架构设备而言,其模块化的架构设计意味着不同的扩展可以拥有各自的优化指令。CPU 的指令集只能在运行时才能得知,在此之前只能使用兼容性最高的指令。“alternative” 在这种情况下是一种非常好的解决方案,既保证了兼容性,也提高了性能。
参考资料
[RISC-V Bit-manipulation A, B, C and S Extensions Five EmbedDev (five-embeddev.com)]001 - Latest corss-compilers
- Linux kernel source tree
- 通过编译器解决因链接过程 KEEP 操作引起的 Section GC 失败问题
- QEMU source tree
- Macro (Using as)
- [PATCH v5 09/13] riscv: switch to relative alternative entries
- [PATCH v5 12/12] RISC-V: fix auipc-jalr addresses in patched alternatives
猜你喜欢:
- 我要投稿:发表原创技术文章,收获福利、挚友与行业影响力
- 知识星球:独家 Linux 实战经验与技巧,订阅「Linux知识星球」
- 视频频道:泰晓学院,B 站,发布各类 Linux 视频课
- 开源小店:欢迎光临泰晓科技自营店,购物支持泰晓原创
- 技术交流:Linux 用户技术交流微信群,联系微信号:tinylab
| 支付宝打赏 ¥9.68元 | 微信打赏 ¥9.68元 | |
 |  请作者喝杯咖啡吧 |  |
Read Album:
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(六):PLIC 和 串口支持
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(五):BootLoader 和设备树
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(四):内存模型和 CPU 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(三):KVM 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(二):库的 RISC-V 适配


