[置顶] 泰晓 RISC-V 实验箱,配套 30+ 讲嵌入式 Linux 系统开发公开课
扁平化设备树(DTB)格式剖析之一:版本,报头和内存保留块
Corrector: TinyCorrect v0.1-rc2 - [spaces urls] Author: iOSDevLog iosdevlog@iosdevlog.com Date: 2022/08/17 Revisor: Fajie.WangNiXi YuHaoW1226@163.com; @taotieren admin@taotieren.com; Falcon falcon@tinylab.org Project: RISC-V Linux 内核剖析 Sponsor: PLCT Lab, ISCAS
扁平化设备树(DTB)由于标准内容较多,故准备分为 3 篇文章进行格式剖析:
- 介绍 DTB 标准前面部分的版本,报头和内存保留块
- 介绍 DTB 标准前面部分的结构体块,字符串块和对齐
- 以一个真实 DTB 文件的部分为例,使用图文结合的方式,详细介绍 DTB 格式展开后生成的设备树结构
Flattened Devicetre (DTB) Format 简介
The Devicetree Blob (DTB) format is a flat binary encoding of devicetree data.
设备树 Blob(DTB)格式是设备树数据的扁平二进制编码。
It used to exchange devicetree data between software programs.
它用于在软件程序之间交换设备树数据。
For example, when booting an operating system, firmware will pass a DTB to the OS kernel.
例如:在启动操作系统时,固件会将 DTB 传递给操作系统内核。
Note
IEEE1275 Open Firmware does not define the DTB format.
On most Open Firmware compliant platforms the devicetree is extracted by calling firmware methods to walk through the tree structure.
注意
IEEE1275 开放固件没有定义 DTB 格式。
在大多数开放固件兼容平台上,通过调用固件方法遍历树结构来提取设备树。
The DTB format encodes the devicetree data within a single, linear, pointerless data structure.
DTB 格式在单个、线性、无指针数据结构中对设备树数据进行编码。
It consists of a small header, followed by three variable sized sections: the memory reservation block, the structure block, and the strings block.
它由一个小报头和三个变长的部分组成:内存保留块、结构体块和字符串块。
These should be present in the flattened devicetree in that order.
这些应该以此顺序出现在扁平化设备树中。
Thus, the devicetree structure as a whole, when loaded into memory at address, will resemble the diagram in Fig. (lower addresses are at the top of the diagram).
因此,设备树结构作为一个整体,当加载到内存地址时,将类似于下方的图(较低的地址在图的顶部)。
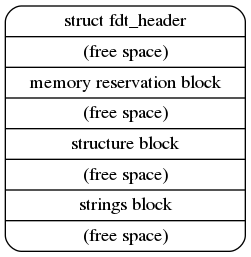
The (free space) sections may not be present, though in some cases they might be required to satisfy the alignment constraints of the individual blocks.
(可用空间)部分可能不存在,但在某些情况下,它们可能需要满足各个块的对齐约束。
Versioning 版本
Several versions of the flattened devicetree structure have been defined since the original definition of the format.
自从“扁平化设备树结构”格式被定义以来,已经发布了多个版本。
Fields in the header give the version, so that the client program can determine if the devicetree is encoded in a compatible format.
报头中的字段给出版本,以便客户端程序能够确定设备树是否以兼容的格式编码。
This document describes only version 17 of the format.
本文仅描述了该格式的第 17 版。
DTSpec compliant boot programs shall provide a devicetree of version 17 or later, and should provide a devicetree of a version that is backwards compatible with version 16.
DTSpec 兼容的引导程序应提供版本 17 或更高版本的设备树,并应提供与版本 16 向下兼容的版本的设备树。
DTSpec compliant client programs shall accept devicetrees of any version backwards compatible with version 17 and may accept other versions as well.
DTSpec 兼容的客户端程序应接受向下兼容版本 17 的任何版本的设备树,并且也可以接受其他版本。
Note
The version is with respect to the binary structure of the device tree, not its content.
注意
版本是关于设备树的二进制结构,而不是它的内容。
Header 报头
The layout of the header for the devicetree is defined by the following C structure.
devicetree 的报头布局被定义为以下 C 结构体。
All the header fields are 32-bit integers, stored in big-endian format.
所有的头字段都是 32 位整数,以大端格式存储。
Flattened Devicetree Header Fields 扁平化设备树报头字段
struct fdt_header {
fdt32_t magic; /* magic word FDT_MAGIC */
fdt32_t totalsize; /* total size of DT block */
fdt32_t off_dt_struct; /* offset to structure */
fdt32_t off_dt_strings; /* offset to strings */
fdt32_t off_mem_rsvmap; /* offset to memory reserve map */
fdt32_t version; /* format version */
fdt32_t last_comp_version; /* last compatible version */
/* version 2 fields below */
fdt32_t boot_cpuid_phys; /* Which physical CPU id we're booting on */
/* version 3 fields below */
fdt32_t size_dt_strings; /* size of the strings block */
/* version 17 fields below */
fdt32_t size_dt_struct; /* size of the structure block */
};
- magic
- This field shall contain the value 0xd00dfeed (big-endian).
- 该字段应包含值 0xd00dfeed(大端)。
- totalsize
- This field shall contain the total size in bytes of the devicetree data structure.
- 该字段应包含设备树数据结构以字节为单位的总大小。
- This size shall encompass all sections of the structure: the header, the memory reservation block, structure block and strings block, as well as any free space gaps between the blocks or after the final block.
- 该大小应包含结构的所有部分:标题、内存保留块、结构体块和字符串块,以及块之间或最后一个块之后的任何空闲空间间隙。
- off_dt_struct
- This field shall contain the offset in bytes of the structure block from the beginning of the header.
- 该字段应包含结构体块从报头开始的以字节为单位的偏移量。
- off_dt_strings
- This field shall contain the offset in bytes of the strings block from the beginning of the header.
- 该字段应包含字符串块从报头开始的以字节为单位的偏移量。
- off_mem_rsvmap
- This field shall contain the offset in bytes of the memory reservation block from the beginning of the header.
- 该字段应包含从报头开始的内存保留块的字节偏移量。
- version
- This field shall contain the version of the devicetree data structure.
- 该字段应包含设备树数据结构的版本。
- The version is 17 if using the structure as defined in this document.
- 如果使用本文中定义的结构,则版本为 17。
- An DTSpec boot program may provide the devicetree of a later version, in which case this field shall contain the version number defined in whichever later document gives the details of that version.
- DTSpec 引导程序可能会提供更高版本的设备树,在这种情况下,该字段应包含在提供该版本详细信息的较晚文档中定义的版本号。
- last_comp_version
- This field shall contain the lowest version of the devicetree data structure with which the version used is backwards compatible.
- 该字段应包含使用的版本向下兼容的设备树数据结构的最低版本。
- So, for the structure as defined in this document (version 17), this field shall contain 16 because version 17 is backwards compatible with version 16, but not earlier versions.
- 因此,对于本文档(版本 17)中定义的结构,该字段应包含 16,因为版本 17 向下兼容版本 16,但不兼容早期版本。
- a DTSpec boot program should provide a devicetree in a format which is backwards compatible with version 16, and thus this field shall always contain 16.
- DTSpec 引导程序应以向下兼容版本 16 的格式提供设备树,因此该字段应始终包含 16。
- boot_cpuid_phys
- This field shall contain the physical ID of the system’s boot CPU.
- 此字段应包含系统引导 CPU 的物理 ID。
- It shall be identical to the physical ID given in the reg property of that CPU node within the devicetree.
- 它应与设备树中该 CPU 节点的 reg 属性中给出的物理 ID 相同。
- size_dt_strings
- This field shall contain the length in bytes of the strings block section of the devicetree blob.
- 该字段应包含设备树 blob 的字符串块部分的字节长度。
- size_dt_struct
- This field shall contain the length in bytes of the structure block section of the devicetree blob.
- 该字段应包含设备树 blob 的结构体块部分的字节长度。
Memory Reservation Block 内存保留块
Purpose 目的
The memory reservation block provides the client program with a list of areas in physical memory which are reserved; that is, which shall not be used for general memory allocations.
内存保留块为客户端程序提供物理内存中保留的区域列表;也就是说,不应将其用于一般内存分配。
It is used to protect vital data structures from being overwritten by the client program.
它用于保护重要数据结构不被客户端程序覆盖。
For example, on some systems with an IOMMU, the TCE (translation control entry) tables initialized by a DTSpec boot program would need to be protected in this manner.
例如:在一些带有 IOMMU 的系统上,由 DTSpec 引导程序初始化的 TCE(转换控制入口)表需要以这种方式进行保护。
Likewise, any boot program code or data used during the client program’s runtime would need to be reserved (e.g., RTAS on Open Firmware platforms).
同样,在客户端程序运行时使用的任何引导程序代码或数据都需要保留(例如:开放固件平台上的 RTAS)。
DTSpec does not require the boot program to provide any such runtime components, but it does not prohibit implementations from doing so as an extension.
DTSpec 不要求引导程序提供任何此类运行时组件,但它不禁止具体实现以扩展的方式来提供。
More specifically, a client program shall not access memory in a reserved region unless other information provided by the boot program explicitly indicates that it shall do so.
更具体地说,客户端程序不应访问保留区域中的内存,除非引导程序提供的其他信息明确指示它应该这样做。
The client program may then access the indicated section of the reserved memory in the indicated manner.
客户端程序然后可以以指定的方式访问保留存储器的所标明的部分。
Methods by which the boot program can indicate to the client program specific uses for reserved memory may appear in this document, in optional extensions to it, or in platform-specific documentation.
引导程序可以向客户端程序指示保留内存的特定用途的方法可能出现在本文档、它的可选扩展或特定于平台的文档中。
The reserved regions supplied by a boot program may, but are not required to, encompass the devicetree blob itself.
引导程序提供的保留区域可以但不要求包含设备树 blob 本身。
The client program shall ensure that it does not overwrite this data structure before it is used, whether or not it is in the reserved areas.
客户端程序应确保在使用之前不会覆盖此数据结构,无论它是否在保留区域中。
Any memory that is declared in a memory node and is accessed by the boot program or caused to be accessed by the boot program after client entry must be reserved.
任何在内存节点中声明并被引导程序访问或在客户端进入后被引导程序访问的内存都必须保留。
Examples of this type of access include (e.g., speculative memory reads through a non-guarded virtual page).
此类访问的示例包括(例如:通过不受保护的虚拟页面进行推测性内存读取)。
This requirement is necessary because any memory that is not reserved may be accessed by the client program with arbitrary storage attributes.
这个要求是必要的,因此引导程序可能会按照需要以直写的方式执行对保留内存的访问。
Any accesses to reserved memory by or caused by the boot program must be done as not Caching Inhibited and Memory Coherence Required (i.e., WIMG = 0bx01x), and additionally for Book III-S implementations as not Write Through Required (i.e., WIMG = 0b001x).
任何通过引导程序或由引导程序引起的对保留内存的访问都必须在不禁止缓存和内存一致性要求(即 WIMG = 0bx01x)的情况下完成,另外对于 III-S(Book III-E Embedded Environment. Section of the Power ISA defining supervisor instructions and related facilities used in embedded Power processor implementations.) 实现,不要求直写(即,WIMG = 0b001x)。
Further, if the VLE storage attribute is supported, all accesses to reserved memory must be done as VLE=0.
此外,如果支持变长编码(Variable-length encoding, VLE)存储属性,则必须在 VLE = 0 时完成对保留内存的所有访问。
This requirement is necessary because the client program is permitted to map memory with storage attributes specified as not Write Through Required, not Caching Inhibited, and Memory Coherence Required (i.e., WIMG = 0b001x), and VLE=0 where supported.
此要求是必要的,因为客户端程序被允许映射具有指定为不要求直写、不禁止缓存和要求内存一致性(即,WIMG = 0b001x)和 VLE = 0 的存储属性的内存。
The client program may use large virtual pages that contain reserved memory.
客户端程序可能会使用包含保留内存的大型虚拟页面。
However, the client program may not modify reserved memory, so the boot program may perform accesses to reserved memory as Write Through Required where conflicting values for this storage attribute are architecturally permissible.
但是,客户端程序可能不会修改保留内存,因此引导程序可能会按照需要以直写的方式执行对保留内存的访问,其中此存储属性的冲突值在体系结构上是允许的。
Format 格式
The memory reservation block consists of a list of pairs of 64-bit big-endian integers, each pair being represented by the following C structure.
内存保留块由一组 64 位大端整数对的列表组成,每对用以下 C 结构体表示。
struct fdt_reserve_entry {
uint64_t address;
uint64_t size;
};
Each pair gives the physical address and size in bytes of a reserved memory region.
每对都提供保留内存区域的物理地址和大小(以字节为单位)。
These given regions shall not overlap each other.
这些给定区域不应相互覆盖。
The list of reserved blocks shall be terminated with an entry where both address and size are equal to 0.
保留块列表应以地址和大小均等于 0 的输入(结构体)结束。
Note that the address and size values are always 64-bit.
注意地址和大小值始终为 64 位。
On 32-bit CPUs the upper 32-bits of the value are ignored.
在 32 位 CPU 上,值的高 32 位被忽略。
Each uint64_t in the memory reservation block, and thus the memory reservation block as a whole, shall be located at an 8-byte aligned offset from the beginning of the devicetree blob.
内存保留块中的每个 uint64_t 以及整个内存保留块都应位于距设备树 blob 开头的 8 字节对齐偏移处。
总结
本文参考 devicetree-specification-v0.4-rc1.pdf 第 5 章介绍扁平化设备树(DTB)格式的的版本,报头和内存保留块相关内容。
下一篇文章继续介绍 DTB 格式的结构体块,字符串块和对齐相关内容。
参考
猜你喜欢:
- 我要投稿:发表原创技术文章,收获福利、挚友与行业影响力
- 知识星球:独家 Linux 实战经验与技巧,订阅「Linux知识星球」
- 视频频道:泰晓学院,B 站,发布各类 Linux 视频课
- 开源小店:欢迎光临泰晓科技自营店,购物支持泰晓原创
- 技术交流:Linux 用户技术交流微信群,联系微信号:tinylab
| 支付宝打赏 ¥9.68元 | 微信打赏 ¥9.68元 | |
 |  请作者喝杯咖啡吧 |  |
Read Album:
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(六):PLIC 和 串口支持
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(五):BootLoader 和设备树
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(四):内存模型和 CPU 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(三):KVM 模型
- Stratovirt 的 RISC-V 虚拟化支持(二):库的 RISC-V 适配


